8.4 Nerve Impulses
Created by CK-12 Foundation/Adapted by Christine Miller

When Lightning Strikes
This amazing cloud-to-surface lightning occurred when a difference in electrical charge built up in a cloud relative to the ground. When the buildup of charge was great enough, a sudden discharge of electricity occurred. A nerve impulse is similar to a lightning strike. Both a nerve impulse and a lightning strike occur because of differences in electrical charge, and both result in an electric current.
Generating Nerve Impulses
A nerve impulse, like a lightning strike, is an electrical phenomenon. A nerve impulse occurs because of a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron. How does this difference in electrical charge come about? The answer involves ions, which are electrically-charged atoms or molecules.
Resting Potential
When a neuron is not actively transmitting a nerve impulse, it is in a resting state, ready to transmit a nerve impulse. During the resting state, the sodium-potassium pump maintains a difference in charge across the cell membrane of the neuron. The sodium-potassium pump is a mechanism of active transport that moves sodium ions (Na+) out of cells and potassium ions (K+) into cells. The sodium-potassium pump moves both ions from areas of lower to higher concentration, using energy in ATP and carrier proteins in the cell membrane. The video below, “Sodium Potassium Pump” by Amoeba Sisters, describes in greater detail how the sodium-potassium pump works. Sodium is the principal ion in the fluid outside of cells, and potassium is the principal ion in the fluid inside of cells. These differences in concentration create an electrical gradient across the cell membrane, called resting potential. Tightly controlling membrane resting potential is critical for the transmission of nerve impulses.
Sodium Potassium Pump, Amoeba Sisters, 2020.
Action Potential
A nerve impulse is a sudden reversal of the electrical gradient across the plasma membrane of a resting neuron. The reversal of charge is called an action potential. It begins when the neuron receives a chemical signal from another cell or some other type of stimulus. If the stimulus is strong enough to reach threshold, an action potential will take place is a cascade along the axon.
This reversal of charges ripples down the axon of the neuron very rapidly as an electric current, which is illustrated in the diagram below (Figure 8.4.2). A nerve impulse is an all-or-nothing response depending on if the stimulus input was strong enough to reach threshold. If a neuron responds at all, it responds completely. A greater stimulation does not produce a stronger impulse.
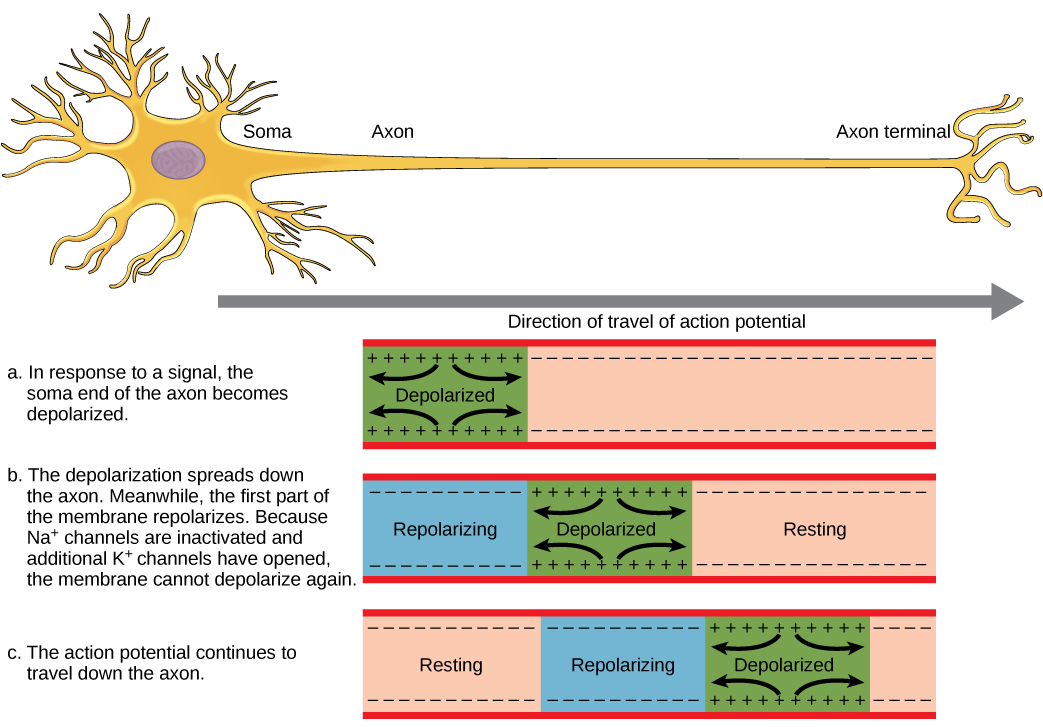
In neurons with a myelin sheath on their axon, ions flow across the membrane only at the nodes between sections of myelin. As a result, the action potential appears to jump along the axon membrane from node to node, rather than spreading smoothly along the entire membrane. This increases the speed at which the action potential travels.
Transmitting Nerve Impulses
The place where an axon terminal meets another cell is called a synapse. This is where the transmission of a nerve impulse to another cell occurs. The cell that sends the nerve impulse is called the presynaptic cell, and the cell that receives the nerve impulse is called the postsynaptic cell.
Some synapses are purely electrical and make direct electrical connections between neurons. Most synapses, however, are chemical synapses. Transmission of nerve impulses across chemical synapses is more complex.
Chemical Synapses
At a chemical synapse, both the presynaptic and postsynaptic areas of the cells are full of molecular machinery that is involved in the transmission of nerve impulses. As shown in Figure 8.4.3, the presynaptic area contains many tiny spherical vessels called synaptic vesicles that are packed with chemicals called neurotransmitters. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of the presynaptic cell, it opens channels that allow calcium to enter the terminal. Calcium causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with the membrane, releasing their contents into the narrow space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes. This area is called the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitter molecules travel across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors, which are proteins embedded in the membrane of the postsynaptic cell.
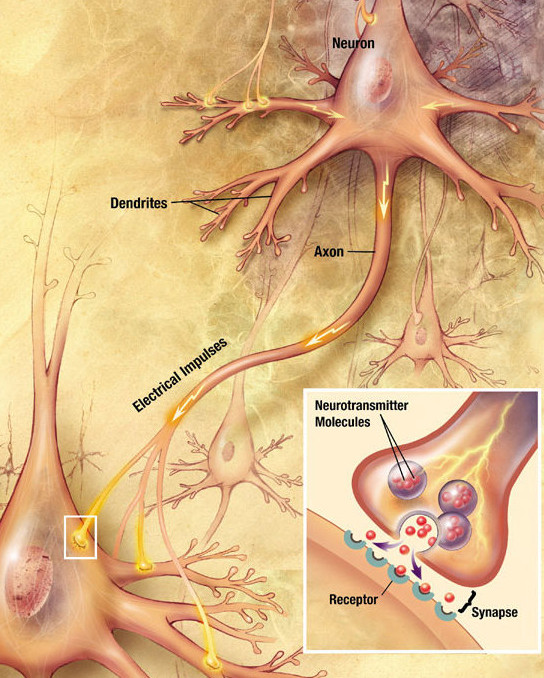
Neurotransmitters and Receptors
There are more than a hundred known neurotransmitters, and more than one type of neurotransmitter may be released at a given synapse by a presynaptic cell. For example, it is common for a faster-acting neurotransmitter to be released, along with a slower-acting neurotransmitter. Many neurotransmitters also have multiple types of receptors to which they can bind. Receptors, in turn, can be divided into two general groups: chemically gated ion channels and second messenger systems.
- When a chemically gated ion channel is activated, it forms a passage that allows specific types of ions to flow across the cell membrane. Depending on the type of ion, the effect on the target cell may be excitatory or inhibitory.
- When a second messenger system is activated, it starts a cascade of molecular interactions inside the target cell. This may ultimately produce a wide variety of complex effects, such as increasing or decreasing the sensitivity of the cell to stimuli, or even altering gene transcription.
The effect of a neurotransmitter on a postsynaptic cell depends mainly on the type of receptors that it activates, making it possible for a particular neurotransmitter to have different effects on various target cells. A neurotransmitter might excite one set of target cells, inhibit others, and have complex modulatory effects on still others, depending on the type of receptors. However, some neurotransmitters have relatively consistent effects on other cells. Consider the two most widely used neurotransmitters, glutamate and GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). Glutamate receptors are either excitatory or modulatory in their effects, whereas GABA receptors are all inhibitory in their effects in adults.
Problems with neurotransmitters or their receptors can cause neurological disorders. The disease myasthenia gravis, for example, is caused by antibodies from the immune system blocking receptors for the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in postsynaptic muscle cells. This inhibits the effects of acetylcholine on muscle contractions, producing symptoms, such as muscle weakness and excessive fatigue during simple activities. Some mental illnesses (including depression) are caused, at least in part, by imbalances of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. One of the neurotransmitters involved in depression is thought to be serotonin, which normally helps regulate mood, among many other functions. Some antidepressant drugs are thought to help alleviate depression in many patients by normalizing the activity of serotonin in the brain.
8.4 Summary
- A nerve impulse is an electrical phenomenon that occurs because of a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron.
- The sodium-potassium pump maintains an electrical gradient across the plasma membrane of a neuron when it is not actively transmitting a nerve impulse. This gradient is called the resting potential of the neuron.
- An action potential is a sudden reversal of the electrical gradient across the plasma membrane of a resting neuron. It begins when the neuron receives a chemical signal from another cell or some other type of stimulus. The action potential travels rapidly down the neuron’s axon as an electric current and occurs in three stages: Depolarization, Repolarization and Recovery.
- A nerve impulse is transmitted to another cell at either an electrical or a chemical synapse. At a chemical synapse, neurotransmitter chemicals are released from the presynaptic cell into the synaptic cleft between cells. The chemicals travel across the cleft to the postsynaptic cell and bind to receptors embedded in its membrane.
- There are many different types of neurotransmitters. Their effects on the postsynaptic cell generally depend on the type of receptor they bind to. The effects may be excitatory, inhibitory, or modulatory in more complex ways. Both physical and mental disorders may occur if there are problems with neurotransmitters or their receptors.
8.4 Review Questions
- Define nerve impulse.
- What is the resting potential of a neuron, and how is it maintained?
- Explain how and why an action potential occurs.
- Outline how a signal is transmitted from a presynaptic cell to a postsynaptic cell at a chemical synapse.
- What generally determines the effects of a neurotransmitter on a postsynaptic cell?
- Identify three general types of effects that neurotransmitters may have on postsynaptic cells.
- Explain how an electrical signal in a presynaptic neuron causes the transmission of a chemical signal at the synapse.
- The flow of which type of ion into a neuron results in an action potential? How do these ions get into the cell? What does this flow of ions do to the relative charge inside the neuron compared to the outside?
- Name three neurotransmitters.
-
-
8.4 Explore More
Action Potentials, Teacher’s Pet, 2018.
TED Ed| What is depression? – Helen M. Farrell, Parta Learning, 2017.
5 Weird Involuntary Behaviors Explained!, It’s Okay To Be Smart, 2015.
Attributions
Figure 8.4.1
Lightening/ Purple Lightning, Dee Why by Jeremy Bishop on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 8.4.2
Action Potential by CNX OpenStax, Biology on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/deed.en) license.
Figure 8.4.3
Chemical_synapse_schema_cropped by Looie496 created file (adapted from original from US National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging) is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
References
Amoeba Sisters. (2020, January 29). Sodium potassium pump. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7NY6XdPBhxo&feature=youtu.be
CNX OpenStax. (2016, May 27) Figure 4 The action potential is conducted down the axon as the axon membrane depolarizes, then repolarizes [digital image]. In Open Stax, Biology (Section 35.2). OpenStax CNX. https://cnx.org/contents/GFy_h8cu@10.53:cs_Pb-GW@6/How-Neurons-Communicate
It’s Okay To Be Smart. (2015, January 26). 5 Weird involuntary behaviors explained! YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZE8sRMZ5BCA&feature=youtu.be
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Depression (major depressive disorder) [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/depression/symptoms-causes/syc-20356007
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Myasthenia gravis [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/myasthenia-gravis/symptoms-causes/syc-20352036
National Institute on Aging. (2006, April 8). Alzheimers disease: Unraveling the mystery. National Institutes of Health. https://www.nia.nih.gov/ (archived version)
Parta Learning. (2017, December 8). TED Ed| What is depression? – Helen M. Farrell. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rBcU_apy0h8&t=291s
Teacher’s Pet. (2018, August 26). Action potentials. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FEHNIELPb0s&feature=youtu.be
A signal transmitted along a nerve fiber.
An atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
The smallest particle of an element that still has the properties of that element.
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
A functional unit of the nervous system that transmits nerve impulses; also called a nerve cell.
A solute pump that pumps potassium into cells while pumping sodium out of cells, both against their concentration gradients. This pumping is active and occurs at the ratio of 2 potassium for every 3 calcium.
The semipermeable membrane surrounding the cytoplasm of a cell.
The movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration, assisted by enzymes and requiring energy.
A complex organic chemical that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, e.g. muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer.
The difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron that is not actively transmitting a nerve impulse.
Reversal of electrical charge across the membrane of a resting neuron that travels down the axon of the neuron as a nerve impulse.
Something that triggers a behavior or other response.
The critical level to which a membrane potential must be depolarized to initiate an action potential.
The place where the axon terminal of a neuron transmits a chemical or electrical signal to another cell.
The cell that sends the nerve impulse.
The cell that receives the nerve impulse.
These membrane-bound organelles store various neurotransmitters that are released at the synapse. The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Vesicles are essential for propagating nerve impulses between neurons and are constantly recreated by the cell.
A type of chemical that transmits signals from the axon of a neuron to another cell across a synapse.
A space that separates two neurons. It forms a junction between two or more neurons and helps nerve impulse pass from one neuron to the other.
A protein on a cell membrane or inside of a cell that binds with a hormone, neurotransmitter, or other chemical signal to produce a response.
A neurotransmitter that will have excitatory effects on the neuron, meaning it will increase the likelihood that a neuron will fire an action potential.
A neurotransmitter that decreases the likelihood that a neuron will fire an action potential.
A chemical that nerve cells use to send signals to other cells. It is by a wide margin the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system.
A naturally occurring amino acid that works as a neurotransmitter in your brain. Neurotransmitters function as chemical messengers. GABA is considered an inhibitory neurotransmitter because it blocks, or inhibits, certain brain signals and decreases activity in your nervous system.
An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large, Y-shaped protein produced mainly by plasma cells that is used by the immune system to neutralize pathogens such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
An organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (and humans) as a neurotransmitter—a chemical message released by nerve cells to send signals to other cells, such as neurons, muscle cells and gland cells.
A neurotransmitter. It has a popular image as a contributor to feelings of well-being and happiness, though its actual biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction.

