16.2 Organs of Excretion
Created by CK-12 Foundation/Adapted by Christine Miller

Getting Rid of Wastes
The many chimneys on these houses are one way that the inhabitants of the home get rid of the wastes they produce. The chimneys expel waste gases that are created when they burn fuel in their furnace or fireplace. Think about the other wastes that people create in their homes and how we dispose of them. Solid trash and recyclables may go to the curb in a trash can, or in a recycling bin for pick up and transport to a landfill or recycling centre. Wastewater from sinks, showers, toilets, and the washing machine goes into a main sewer pipe and out of the house to join the community’s sanitary sewer system.
Like a busy home, your body also produces a lot of wastes that must be eliminated. Like a home, the way your body gets rid of wastes depends on the nature of the waste products. Some human body wastes are gases, some are solids, and some are in a liquid state. Getting rid of body wastes is called excretion, and there are a number of different organs of excretion in the human body.
Excretion
Excretion is the process of removing wastes and excess water from the body. It is an essential process in all living things, and it is one of the major ways the human body maintains homeostasis. It also helps prevent damage to the body. Wastes include by-products of metabolism — some of which are toxic — and other non-useful materials, such as used up and broken down components. Some of the specific waste products that must be excreted from the body include carbon dioxide from cellular respiration, ammonia and urea from protein catabolism, and uric acid from nucleic acid catabolism.
Excretory Organs
Organs of excretion include the skin, liver, large intestine, lungs, and kidneys (see Figure 16.2.2). Together, these organs make up the excretory system. They all excrete wastes, but they don’t work together in the same way that organs do in most other body systems. Each of the excretory organs “does its own thing” more-or-less independently of the others, but all are necessary to successfully excrete the full range of wastes from the human body.
Figure 16.2.2 Internal organs of excretion are identified in this illustration. They include the skin, liver, large intestine, lungs, and kidneys.
Skin

The skin is part of the integumentary system, but it also plays a role in excretion through the production of sweat by sweat glands in the dermis. Although the main role of sweat production is to cool the body and maintain temperature homeostasis, sweating also eliminates excess water and salts, as well as a small amount of urea. When sweating is copious, as in Figure 16.2.3, ingestion of salts and water may be helpful to maintain homeostasis in the body.
Liver
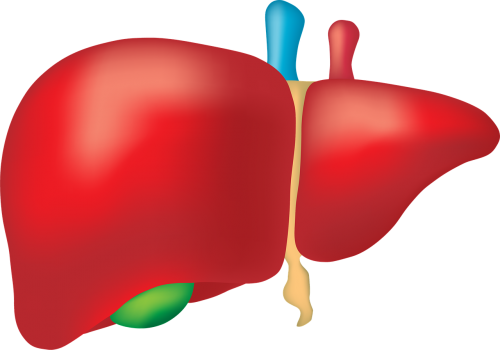
The liver (shown in Figure 16.2.4) has numerous major functions, including secreting bile for digestion of lipids, synthesizing many proteins and other compounds, storing glycogen and other substances, and secreting endocrine hormones. In addition to all of these functions, the liver is a very important organ of excretion. The liver breaks down many substances in the blood, including toxins. For example, the liver transforms ammonia — a poisonous by-product of protein catabolism — into urea, which is filtered from the blood by the kidneys and excreted in urine. The liver also excretes in its bile the protein bilirubin, a byproduct of hemoglobin catabolism that forms when red blood cells die. Bile travels to the small intestine and is then excreted in feces by the large intestine.
Large Intestine
The large intestine is an important part of the digestive system and the final organ in the gastrointestinal tract. As an organ of excretion, its main function is to eliminate solid wastes that remain after the digestion of food and the extraction of water from indigestible matter in food waste. The large intestine also collects wastes from throughout the body. Bile secreted into the gastrointestinal tract, for example, contains the waste product bilirubin from the liver. Bilirubin is a brown pigment that gives human feces its characteristic brown colour.
Lungs
The lungs are part of the respiratory system (shown in Figure 16.2.5), but they are also important organs of excretion. They are responsible for the excretion of gaseous wastes from the body. The main waste gas excreted by the lungs is carbon dioxide, which is a waste product of cellular respiration in cells throughout the body. Carbon dioxide is diffused from the blood into the air in the tiny air sacs called alveoli in the lungs (shown in the inset diagram). By expelling carbon dioxide from the blood, the lungs help maintain acid-base homeostasis. In fact, it is the pH of blood that controls the rate of breathing. Water vapor is also picked up from the lungs and other organs of the respiratory tract as the exhaled air passes over their moist linings, and the water vapor is excreted along with the carbon dioxide. Trace levels of some other waste gases are exhaled, as well.
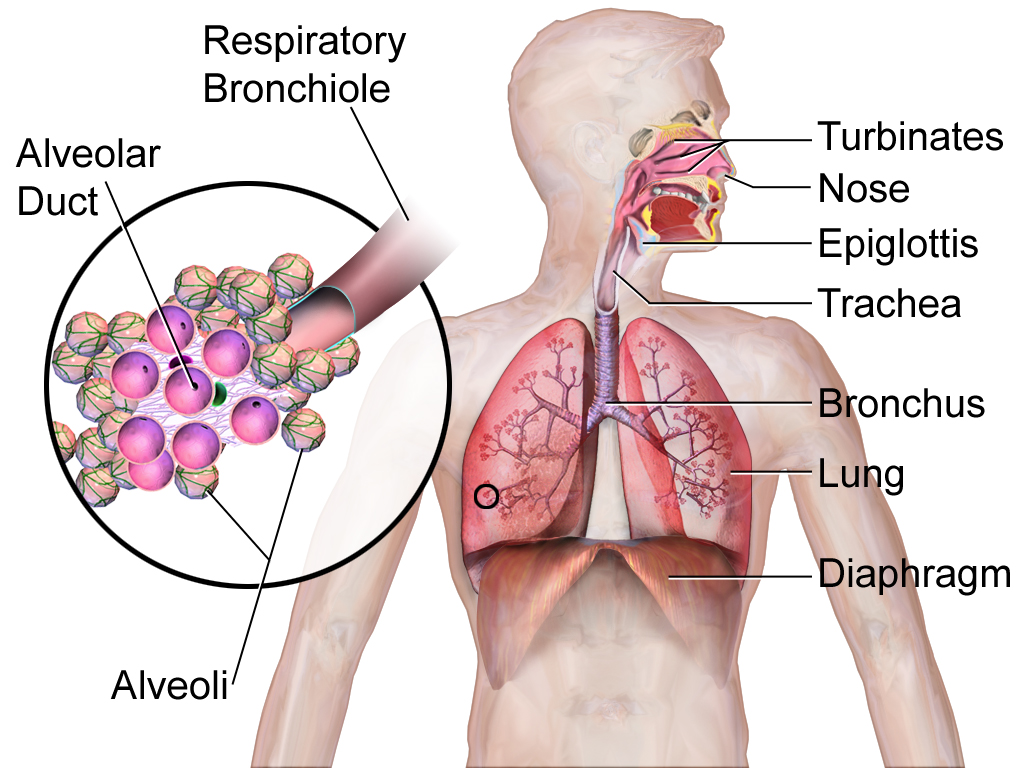
Kidneys
The paired kidneys are often considered the main organs of excretion. The primary function of the kidneys is the elimination of excess water and wastes from the bloodstream by the production of the liquid waste known as urine. The main structural and functional units of the kidneys are tiny structures called nephrons. Nephrons filter materials out of the blood, return to the blood what is needed, and excrete the rest as urine. As shown in Figure 16.2.6, the kidneys are organs of the urinary system, which also includes the ureters, bladder, and urethra — organs that transport, store, and eliminate urine, respectively.
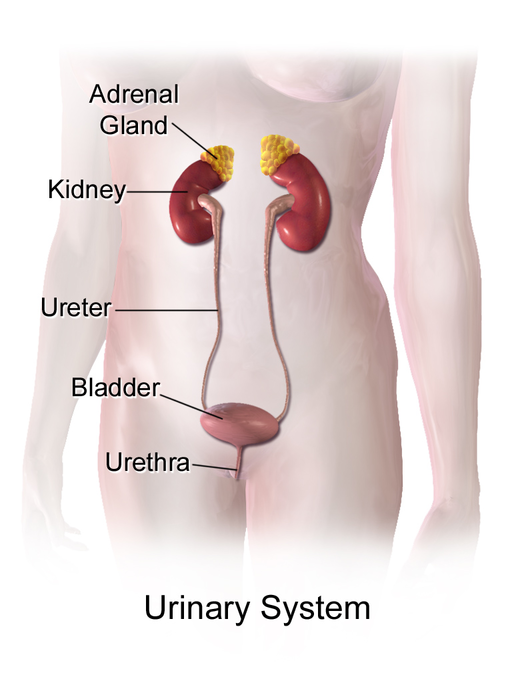
By producing and excreting urine, the kidneys play vital roles in body-wide homeostasis. They maintain the correct volume of extracellular fluid, which is all the fluid in the body outside of cells, including the blood and lymph. The kidneys also maintain the correct balance of salts and pH in extracellular fluid. In addition, the kidneys function as endocrine glands, secreting hormones into the blood that control other body processes. You can read much more about the kidneys in section 16.4 Kidneys.
16.2 Summary
- Excretion is the process of removing wastes and excess water from the body. It is an essential process in all living things and a major way the human body maintains homeostasis.
- Organs of excretion include the skin, liver, large intestine, lungs, and kidneys. All of them excrete wastes, and together they make up the excretory system.
- The skin plays a role in excretion through the production of sweat by sweat glands. Sweating eliminates excess water and salts, as well as a small amount of urea, a byproduct of protein catabolism.
- The liver is a very important organ of excretion. The liver breaks down many substances in the blood, including toxins. The liver also excretes bilirubin — a waste product of hemoglobin catabolism — in bile. Bile then travels to the small intestine, and is eventually excreted in feces by the large intestine.
- The main excretory function of the large intestine is to eliminate solid waste that remains after food is digested and water is extracted from the indigestible matter. The large intestine also collects and excretes wastes from throughout the body, including bilirubin in bile.
- The lungs are responsible for the excretion of gaseous wastes, primarily carbon dioxide from cellular respiration in cells throughout the body. Exhaled air also contains water vapor and trace levels of some other waste gases.
- The paired kidneys are often considered the main organs of excretion. Their primary function is the elimination of excess water and wastes from the bloodstream by the production of urine. The kidneys contain tiny structures called nephrons that filter materials out of the blood, return to the blood what is needed, and excrete the rest as urine. The kidneys are part of the urinary system, which also includes the ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
16.2 Review Questions
- What is excretion, and what is its significance?
-
- Describe the excretory functions of the liver.
- What are the main excretory functions of the large intestine?
- List organs of the urinary system.
- Describe the physical states in which the wastes from the human body are excreted.
- Give one example of why ridding the body of excess water is important.
- What gives feces its brown colour? Why is that substance produced?
16.2 Explore More
Why Can We Regrow A Liver (But Not A Limb)? MITK12Videos, 2015.
Are Sports Drinks Good For You? | Fit or Fiction, POPSUGAR Fitness, 2014.
Why do we sweat? – John Murnan, TED-Ed, 2018.
Attributions
Figure 16.2.1
Chimneys/ Kingston upon Hull, England [photo] by Angela Baker on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 16.2.2
- Sweat or rain? by Kullez on Flickr is used under a CC BY 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/).
- Kidney front – white from www.medicalgraphics.de is used under a CC BY-ND 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/) license.
- File:Liver Cirrhosis.png by BruceBlaus on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en) license.
- File:Human lungs.png by Sharanyaudupa on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en) license.
- Tags: Offal Marking Medical Intestine Liver by Elionas2 on Pixabay is used under the Pixabay license (https://pixabay.com/service/license/).
Figure 16.2.3
gym_room_fitness_equipment_cardiovascular_exercise_elliptical_bike_cardio_training_sports_equipment_bodybuilding-825364 from Pxhere is used under a CC0 1.0 Universal public domain dedication license (https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/).
Figure 16.2.4
Tags: Liver Organ Anatomy by zachvanstone8 on Pixabay is used under the Pixabay License (https://pixabay.com/service/license/).
Figure 16.2.5
Lung_and_diaphragm by Terese Winslow/ National Cancer Institute on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 16.2.6
512px-Urinary_System_(Female) by BruceBlaus on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) license.
References
MITK12Videos. (2015, June 4). Why can we regrow a liver (but not a limb)? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=erMCADOJcHk&feature=youtu.be
POPSUGAR Fitness. (2014, February 7). Are sports drinks good for you? | Fit or Fiction. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SeK0zFB9yHg&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2018, May 15). Why do we sweat? – John Murnan. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fctH_1NuqCQ&feature=youtu.be
The process of removing wastes and excess water from the body.
The ability of an organism to maintain constant internal conditions despite external changes.
The chemical processes that occur in a living organism to sustain life.
A set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
A compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH3. It is a common nitrogenous waste produced by the breakdown of amino acids in various cells in the body.
Waste product of protein catabolism that is mainly filtered from blood in the kidneys and excreted in urine.
A waste product of nucleic acid catabolism that is mainly filtered from blood by the kidneys and excreted in urine.
The major organ of the integumentary system that covers and protects the body and helps maintain homeostasis, for example, by regulating body temperature.
An organ of digestion and excretion that secretes bile for lipid digestion and breaks down excess amino acids and toxins in the blood.
An organ of the digestive system that removes water and salts from food waste and forms solid feces for elimination.
Two paired organs of the respiratory system in which gas exchange takes place between the blood and the atmosphere.
One of a pair of organs of the excretory and urinary systems that filters wastes and excess water out of blood and forms urine.
The body system responsible for the elimination of wastes produced by homeostasis. There are several parts of the body that are involved in this process, such as sweat glands, the liver, the lungs and the kidney system. ... From there, urine is expelled through the urethra and out of the body.
Salty fluid secreted into ducts by sweat glands in the dermis that excretes wastes and helps cool the body; also called perspiration.
Fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gall bladder that is secreted into the small intestine to help digest lipids and neutralize acid from the stomach.
A multi-branched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria.
The breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones.
A brown pigment secreted into bile by the liver that is a byproduct of catabolism of dead red blood cells and is excreted in feces by the large intestine.
An oxygen-binding protein containing iron that is the principal component of red blood cells.
Solid waste that remains after food is digested and that is eliminated from the body through the anus.
One of a cluster of tiny sacs at the ends of bronchioles in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place.
A liquid waste product of the body that is formed by the kidneys and excreted by the other organs of the urinary system.
One of the million tiny structural and functional units of the kidney that filters blood and forms urine.
A long, narrow, tube-like organ of the digestive system where most chemical digestion of food and virtually all absorption of nutrients take place.

