13.7 Case Study Conclusion: Cough That Won’t Quit
Created by CK-12 Foundation/Adapted by Christine Miller

Case Study Conclusion: Cough That Won’t Quit
Inhaling the moist air from a humidifier or steamy shower can feel particularly good if you have a respiratory system infection, such as bronchitis. The moist air helps to loosen and thin mucus in the respiratory system, allowing you to breathe easier.
In the beginning of this chapter, you learned about Erica, who developed acute bronchitis after getting a cold. She had a worsening cough, a sore throat due to coughing, and chest congestion. She was also coughing up thick mucus.
Acute bronchitis usually occurs after a cold or flu, usually due to the same viruses that cause cold or flu. Because bronchitis is not usually caused by bacteria (although it can be), in most cases, antibiotics are not an effective treatment.
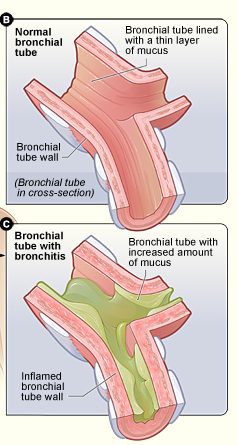
Bronchitis affects the bronchial tubes, which, as you have learned, are air passages in the lower respiratory tract. The main bronchi branch off of the trachea and then branch into smaller bronchi, and then bronchioles. In bronchitis, the walls of the bronchi become inflamed, which makes them narrower. There is also excessive production of mucus in the bronchi, which further narrows the pathway where air can flow through. Figure 13.7.2, shows how bronchitis affects the bronchial tubes.
The treatment for most cases of bronchitis involves thinning and loosening the mucus so that it can be effectively coughed out of the airways. This can be done by drinking plenty of fluids, using humidifiers or steam, and — in some cases — using over-the-counter medications (such as expectorants). Dr. Choo recommended some of these treatments to Erica, and also warned against using cough suppressants. Cough suppressants work on the nervous system to suppress the cough reflex. When a patient has a “productive” cough (which means they are coughing up mucus), doctors generally advise them not to take cough suppressants, so that they can cough the mucus out of their bodies.
When Dr. Choo was examining Erica, she used a pulse oximeter to measure the oxygen level in her blood. Why did she do this? As you have learned, the bronchial tubes branch into bronchioles, which ultimately branch into the alveoli of the lungs. The alveoli are where gas exchange occurs between the air and the blood to take in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide and other wastes. By checking Erica’s blood oxygen level, Dr. Choo was making sure that her clogged airways were not impacting her level of much-needed oxygen.
Erica has acute bronchitis, but you may recall that chronic bronchitis was discussed earlier in this chapter (Section 13.5) as a term that describes the symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). COPD is often due to tobacco smoking, and it causes damage to the walls of the alveoli. Acute bronchitis, on the other hand, typically occurs after a cold or flu, and involves inflammation and mucus build-up in the bronchial tubes. As implied by the difference in their names, chronic bronchitis is an ongoing, long-term condition, while acute bronchitis is likely to resolve relatively quickly with proper rest and treatment.
Erica uses e-cigarettes (vaping), so she is more likely to develop chronic respiratory conditions, such as COPD. As you have learned, smoking damages the respiratory system, along with many other systems of the body. Smoking and vaping increases the risk of respiratory infections, including bronchitis and flu, due to its damaging effects on the respiratory and immune systems. Dr. Choo strongly encouraged Erica to quit vaping, not only so that her acute bronchitis resolves, but so that she can avoid future infections and other negative health outcomes associated with vaping and smoking, including COPD and lung cancer.
As you have learned in this chapter, the respiratory system is critical to carry out the gas exchange necessary for life’s functions, and to protect the body from pathogens and other potentially harmful substances in the air. But this ability to interface with the outside air has a cost. The respiratory system is prone to infections, as well as damage and other negative effects from allergens, mold, air pollution, cigarette smoke and vaping. While exposure to most of these things cannot be avoided, not smoking is an important step you can take to protect this organ system — as well as many other systems of your body.
Chapter 13 Summary
In this chapter, you learned about the respiratory system. Specifically, you learned that:
- Respiration is the process in which oxygen moves from the outside air into the body, and carbon dioxide and other waste gases move from inside the body to the outside air. It involves two subsidiary processes: ventilation and gas exchange.
- The organs of the respiratory system form a continuous system of passages, called the respiratory tract. It has two major divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract.
-
- The upper respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx. All of these organs are involved in conduction, or the movement of air into and out of the body. Incoming air is also cleaned, humidified, and warmed as it passes through the upper respiratory tract. The larynx is also called the voice box, because it contains the vocal cords, which are needed to produce vocal sounds.
- The lower respiratory tract includes the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles, and the lungs. The trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles are involved in conduction. Gas exchange takes place only in the lungs, which are the largest organs of the respiratory tract. Lung tissue consists mainly of tiny air sacs called alveoli, which is where gas exchange takes place between air in the alveoli and the blood in capillaries surrounding them.
- The respiratory system protects itself from potentially harmful substances in the air by the mucociliary escalator. This includes mucus-producing cells, which trap particles and pathogens in incoming air. It also includes tiny hair-like cilia that continually move to sweep the mucus and trapped debris away from the lungs and toward the outside of the body.
- The level of carbon dioxide in the blood is monitored by cells in the brain. If the level becomes too high, it triggers a faster rate of breathing, which lowers the level to the normal range. The opposite occurs if the level becomes too low. The respiratory system exchanges gases with the outside air, but it needs the cardiovascular system to carry the gases to and from cells throughout the body.
- Breathing, or ventilation, is the two-step process of drawing air into the lungs (inhalation) and letting air out of the lungs (exhalation). Inhaling is an active process that results mainly from contraction of a muscle called the diaphragm. Exhaling is typically a passive process that occurs mainly due to the elasticity of the lungs when the diaphragm relaxes.
-
- Breathing is one of the few vital bodily functions that can be controlled consciously, as well as unconsciously. Conscious control of breathing is common in many activities, including swimming and singing. However, there are limits on the conscious control of breathing. If you try to hold your breath, for example, you will soon have an irrepressible urge to breathe.
- Unconscious breathing is controlled by respiratory centers in the medulla and pons of the brainstem. They respond to variations in blood pH by either increasing or decreasing the rate of breathing as needed to return the pH level to the normal range.
- Nasal breathing is generally considered to be superior to mouth breathing, because it does a better job of filtering, warming, and moistening incoming air. It also results in slower emptying of the lungs, which allows more oxygen to be extracted from the air.
- Gas exchange is the biological process through which gases are transferred across cell membranes to either enter or leave the blood. Gas exchange takes place continuously between the blood and cells throughout the body, and also between the blood and the air inside the lungs.
-
- Gas exchange in the lungs takes place in alveoli. The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it travels through pulmonary capillaries, picking up oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. The oxygenated blood then leaves the lungs through pulmonary veins.
- Gas exchange occurs by diffusion across cell membranes. Gas molecules naturally move down a concentration gradient from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This is a passive process that requires no energy.
- Gas exchange by diffusion depends on the large surface area provided by the hundreds of millions of alveoli in the lungs. It also depends on a steep concentration gradient for oxygen and carbon dioxide. This gradient is maintained by continuous blood flow and constant breathing.
- Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways in the lungs, in which the airways periodically become inflamed. This causes swelling and narrowing of the airways, often with excessive mucus production, leading to difficulty breathing and other symptoms. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Asthma attacks are triggered by allergens, air pollution, or other factors.
- Pneumonia is a common inflammatory disease of the respiratory tract in which inflammation affects primarily the alveoli, which become filled with fluid that inhibits gas exchange. Most cases of pneumonia are caused by viral or bacterial infections. Vaccines are available to prevent pneumonia. Treatment often includes prescription antibiotics.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a lung disease characterized by chronic poor airflow, which causes shortness of breath and a productive cough. It is caused most often by tobacco smoking, which leads to breakdown of connective tissues in the lungs. Alveoli are reduced in number and elasticity, making it impossible to fully exhale air from the lungs. There is no cure for COPD, but stopping smoking may reduce the rate at which COPD worsens.
- Lung cancer is a malignant tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. It results from accumulated DNA damage, most often caused by tobacco smoking. Lung cancer is typically diagnosed late, so most cases cannot be cured. It may be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, and/or radiation therapy.
- Smoking is the single greatest cause of preventable death worldwide. It has adverse effects on just about every body system and organ. Tobacco smoke affects not only smokers, but also non-smokers who are exposed to secondhand smoke. The nicotine in tobacco is highly addictive, making it very difficult to quit smoking.
-
- A major health risk of smoking is lung cancer. Smoking also increases the risk of many other types of cancer. Tobacco smoke contains dozens of chemicals that are known carcinogens.
- Smoking is the primary cause of COPD. Chemicals — such as carbon monoxide and cyanide in tobacco smoke — reduce the elasticity of alveoli so the lungs can no longer fully exhale air.
- Smoking and/or vaping damages the cardiovascular system and increases the risk of high blood pressure, blood clots, heart attack, and stroke. Smoking also has a negative impact on blood lipid levels.
- A wide diversity of additional adverse health effects — such as erectile dysfunction, female infertility, and slow wound healing — are attributable to smoking.
As you have learned, the respiratory system brings in oxygen to the body and removes waste gases to the atmosphere — but these molecules wouldn’t get to where they need to go without the cardiovascular system to transport them via the bloodstream. Read the next chapter to learn about how the cardiovascular system carries out these critical functions.
Chapter 13 Review
-
- Describe the relationship between the bronchi, secondary bronchi, tertiary bronchi, and bronchioles.
- Deoxygenated and oxygenated blood both travel to the lungs. Describe what happens to that blood when it gets to the lungs.
- Explain the difference between ventilation and gas exchange.
- Which way do oxygen and carbon dioxide flow during gas exchange in the lungs, and why? Which way do oxygen and carbon dioxide flow during gas exchange between the blood and the body’s cells, and why?
- Why does the body require oxygen, and why does it emit carbon dioxide as a waste product?
- What do coughing and sneezing have in common?
- COPD can cause too much carbon dioxide in the blood. Answer the following questions about this:
- How does COPD cause there to be too much carbon dioxide in the blood?
- What does this do to the blood pH?
- How does the body respond to this change in blood pH?
- What are three different types of things that can enter the respiratory system and cause illness or injury? Describe the negative health effects of each in your answer.
- Where are the respiratory centers of the brain located? What is the main function of the respiratory centers of the brain?
- Smoking increases the risk of getting influenza, commonly known as the flu. Explain why this could lead to a greater risk of pneumonia.
- If a person has a gene that caused them to get asthma, could changes to their environment (such as more frequent cleaning) help their asthma? Why or why not?
- Explain why nasal breathing generally stops particles from entering the body at an earlier stage than mouth breathing does.
Attributions
Figure 13.7.1
Tags: Essential Oils Aroma Diffuser Diffuse Led by asundermeier on Pixabay is used under the Pixabay License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 13.7.2
Bronchitis by National Heart Lung and Blood Institute on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
A tiny, nonliving particle that contains nucleic acids but lacks other characteristics of living cells and may cause human disease.
Any member of a large group of unicellular microorganisms which have cell walls but lack organelles and an organized nucleus, including some which can cause disease.
A lung disease characterized by chronic poor airflow, most often following years of tobacco smoking.
The exchange of gases between the body and the outside air.
The process of moving air into and out of the lungs; also called breathing.
Biological process through which gases are transferred across cell membranes to either enter or leave the blood.
The continuous system of passages through which air flows into and out of the body.
Refers to following airway structures: nasal cavities and passages (sinuses), pharynx, tonsils, and larynx (voice box).
A large, air-filled space in the skull above and behind the nose that helps conduct air in and out of the body as part of the upper respiratory tract.
Tubular organ that connects the mouth and nasal cavity with the larynx and through which air and food pass.
An organ of the respiratory system between the pharynx and trachea, also called the voice box because it contains the vocal cords that allow the production of vocal sounds.
The movement of air into and out of the body.
Two folded pairs of membranes in the larynx (voice box) that vibrate when air that is exhaled passes through them, producing sound.
Refers to following airway structures: trachea (windpipe) and lungs with its substructures bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli.
A tubular organ of the respiratory system that carries air between the larynx and bronchi; also called windpipe.
One of many tubes of various sizes that carry air between the trachea and the alveoli in the lungs.
Any of the minute branches into which a bronchus divides.
Two paired organs of the respiratory system in which gas exchange takes place between the blood and the atmosphere.
One of a cluster of tiny sacs at the ends of bronchioles in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place.
Term for the apparatus of mucus and cilia responsible for movement of mucus up and out of the respiratory tract. Mucus traps particles and cilia propel mucus up and out of the lungs where the fluid and mucus is then swallowed and the debris eliminated by the digestive system.
Tiny hairlike organelles, identical in structure to flagella, that line the surfaces of certain cells and beat in rhythmic waves, providing locomotion to ciliate protozoans and moving liquids along internal epithelial tissue in animals.
The central nervous system organ inside the skull that is the control center of the nervous system.
Inhalation happens when air or other gases enter the lungs. The action of inhaling or breathing in.
The action of exhaling or breathing out. Exhalation happens when air or other gases exit the lungs.
A large, dome-shaped muscle below the lungs that allows breathing to occur when it alternately contracts and relaxes.
A long stem-like structure which makes up part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing.
Part of the central nervous system, located at the base of the brain, between the medulla oblongata and the midbrain. It is part of the brainstem. The pons serves as a message station between several areas of the brain. It helps relay messages from the cortex and the cerebellum
A measure of the acidity or basicity of aqueous or other liquid solutions. The term translates the values of the concentration of the hydrogen ion in a scale ranging from 0 and 14. In pure water, which is neutral (neither acidic nor alkaline), the concentration of the hydrogen ion corresponds to a pH of 7. A solution with a pH less than 7 is considered acidic; a solution with a pH greater than 7 is considered basic, or alkaline.
The semipermeable membrane surrounding the cytoplasm of a cell.
The movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Chronic inflammatory disease of the respiratory system in which airways periodically become inflamed, causing swelling and narrowing of the airways, which makes breathing difficult.
A disease in which the alveoli of the lungs become inflamed and filled with fluid, usually as a result of infection, causing symptoms such as shortness of breath, coughing, chest pain, and fever.
A malignant tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung.

