18.7 Functions of the Female Reproductive System
Created by CK-12 Foundation/Adapted by Christine Miller
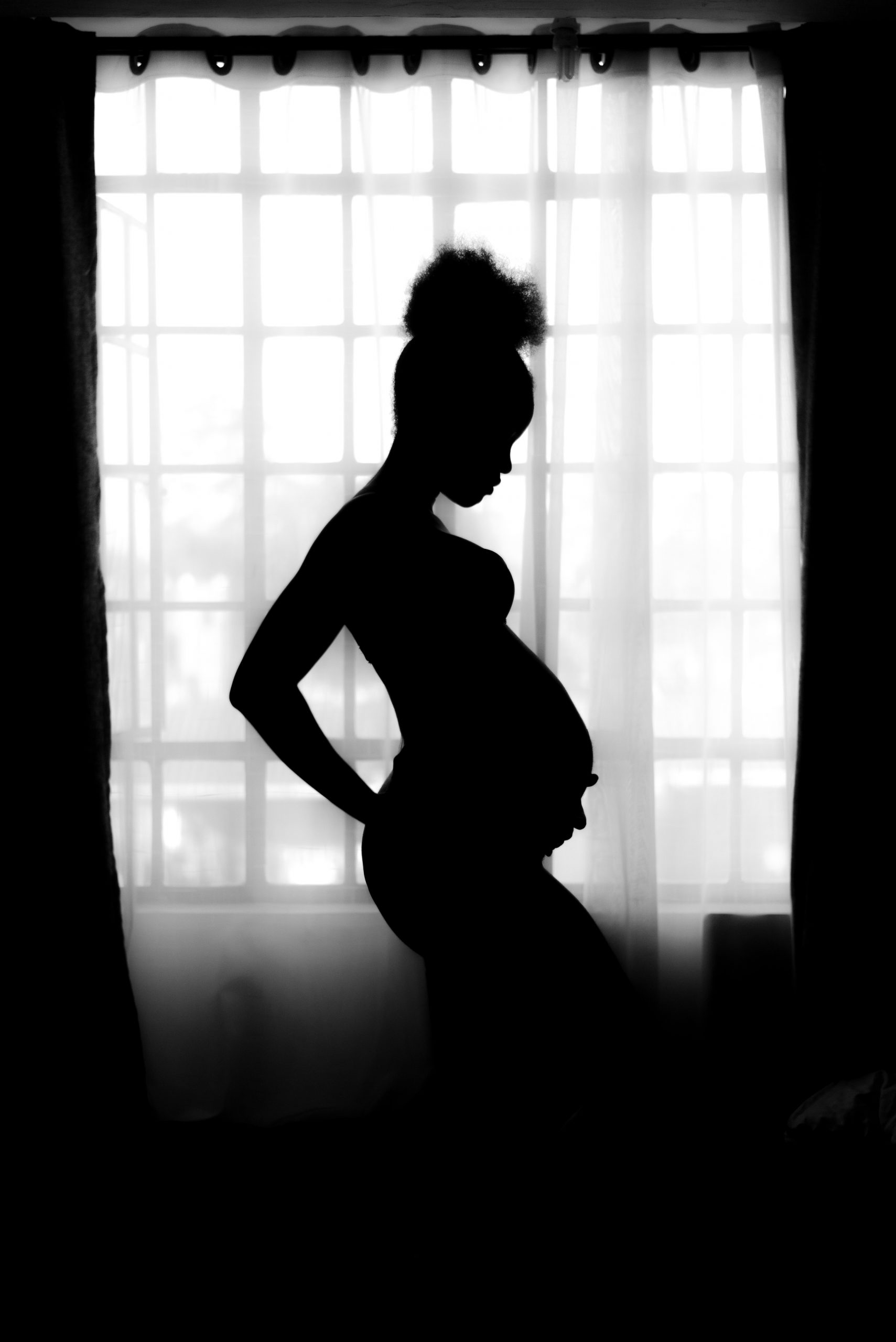

Waiting Expectantly
A mother-to-be waits patiently for her baby to grow as her belly gradually swells. Reproduction is all about making babies, and the female reproductive system is specialized for this purpose. Its functions include producing female gametes called ova, secreting female sex hormones (such as estrogen), providing a site for fertilization, gestating a fetus if fertilization occurs, giving birth to a baby, and breastfeeding a baby after birth. The only thing missing is sperm.
Ova Production
At birth, a female’s ovaries contain all the ova she will ever produce, which may include a million or more ova. The ova don’t start to mature, however, until she enters puberty and attains sexual maturity. After that, one ovum typically matures each month, and is released from an ovary. This continues until a woman reaches menopause (cessation of monthly periods), typically by age 52. By then, viable eggs may be almost depleted, and hormone levels can no longer support the monthly cycle. During the reproductive years, which of the two ovaries releases an egg in a given month seems to be a matter of chance. Occasionally, both ovaries will release an egg at the same time. If both eggs are fertilized, the offspring are fraternal twins (dizygotic, or “two-zygote,” twins), and they are no more alike genetically than non-twin siblings.
Oogenesis
The process of producing ova in the ovaries of a female fetus is called oogenesis. Ova are haploid gametes, and their production occurs in several steps that involve different types of cells, as summarized in Figure 18.7.2. Oogenesis is completed long before birth. It occurs when diploid germ cells called oogonia (singular, oogonium) undergo mitosis. Each such cell division produces two diploid daughter cells. One is called the primary oocyte, and the other is retained to help maintain a reserve of oogonia. The primary oocyte, in turn, starts to go through the first cell division of meiosis (meiosis I). However, it does not complete meiosis I until much later. Instead, it remains in a resting state, nestled within a tiny, immature follicle in the ovary until the female goes through puberty.
Maturation of a Follicle
Beginning in puberty, about once a month, one of the follicles in an ovary undergoes maturation, and an egg is released. As the follicle matures, it goes through changes in the numbers and types of its cells, as shown in Figure 18.7.2. The primary oocyte within the follicle also resumes meiosis. It completes meiosis I, which began long before birth, to form a secondary oocyte and a smaller cell, called the first polar body. Both the secondary oocyte and the first polar body are haploid cells. The secondary oocyte has most of the cytoplasm from the primary oocyte and is much larger than the first polar body, which soon disintegrates and disappears. The secondary oocyte begins meiosis II, but only completes it if the egg is fertilized.
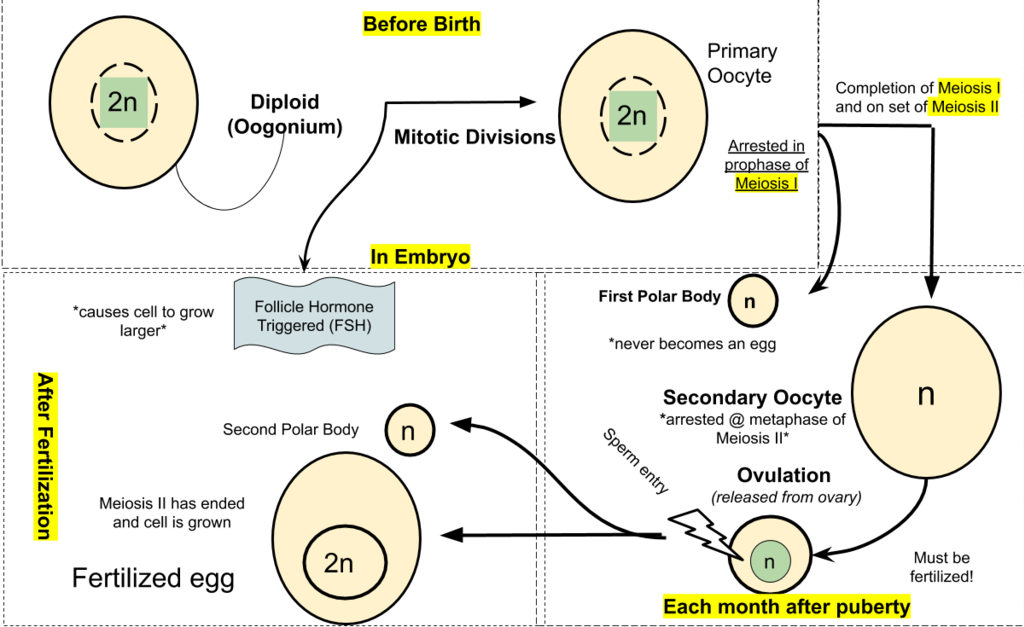
Release of an Egg
It typically takes 12 to 14 days for a follicle to mature in an ovary, and for the secondary oocyte to form. Then, the follicle bursts open and the ovary ruptures, releasing the secondary oocyte from the ovary. This event is called ovulation. The now-empty follicle starts to change into a structure called a corpus luteum. The expelled secondary oocyte is usually swept into the nearby oviduct by its waving, fringe-like fimbriae.
Uterine Changes
While the follicle is maturing in the ovary, the uterus is also undergoing changes to prepare it for an embryo if fertilization occurs. For example, the endometrium gets thicker and becomes more vascular. Around the time of ovulation, the cervix undergoes changes that help sperm reach the ovum to fertilize it. The cervical canal widens, and cervical mucus becomes thinner and more alkaline. These changes help promote the passage of sperm from the vagina into the uterus and make the environment more hospitable to sperm.
Fertilization — or Not
Fertilization of an ovum by a sperm normally occurs in an oviduct, most often in the part of the tube that passes above the ovary (see Figure 18.7.3). In order for fertilization to occur, sperm must “swim” from the vagina where they are deposited, through the cervical canal to the uterus, and then through the body of the uterus to one of the oviducts. Once sperm enter a oviduct, tubular fluids help carry them through the tube toward the secondary oocyte at the other end. The secondary oocyte also functions to promote fertilization. It releases molecules that guide the sperm and allow the surface of the ovum to attach to the surface of the sperm. The ovum can then absorb the sperm, allowing fertilization to occur.
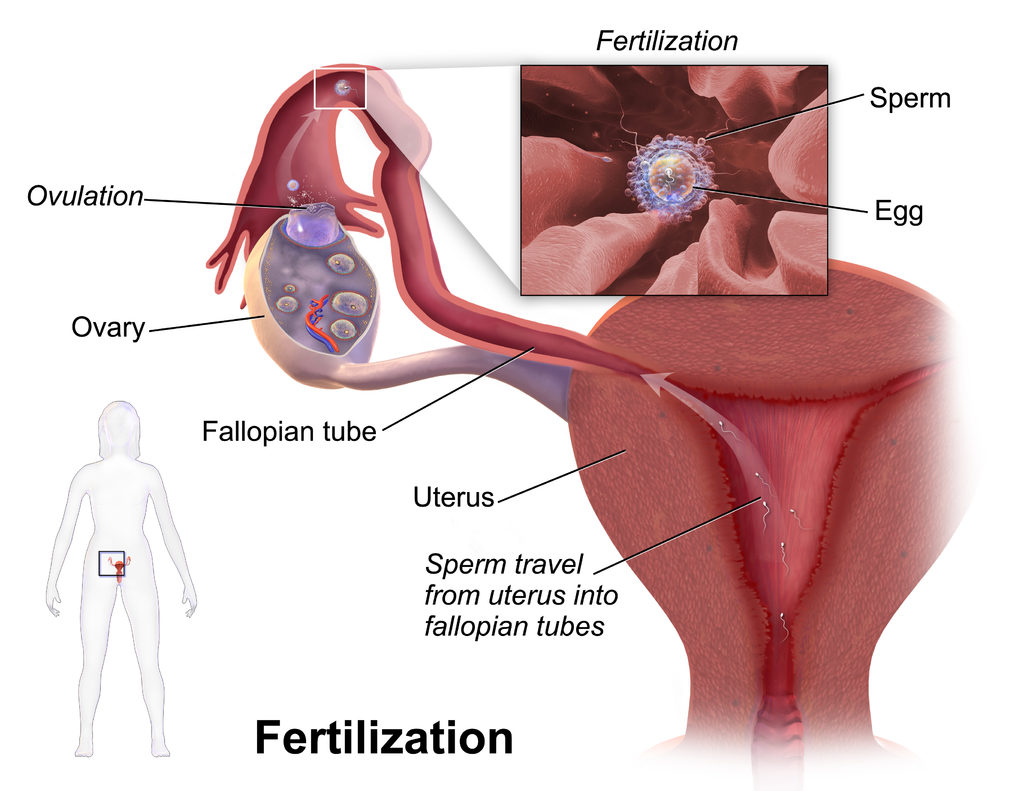
If Fertilization Occurs
If the secondary oocyte is fertilized by a sperm as it passes through the oviduct, the secondary oocyte quickly completes meiosis II, forming a diploid zygote and another polar body. This second polar body, like the first, normally breaks down and disappears. The zygote then continues the journey through the oviduct to the uterus, during which it undergoes several mitotic cell divisions. By the time it reaches the uterus up to five days after fertilization, it consists of a ball of cells called a blastocyst. Within another day or two, the blastocyst implants itself in the endometrium lining the uterus, and gestation begins.
If Fertilization Does Not Occur
What happens if the secondary oocyte is not fertilized by a sperm as it passes through the oviduct? It continues on its way to the uterus without ever completing meiosis II. It is likely to disintegrate within a few days while still in the oviduct. Any remaining material will be shed from the woman’s body during the next menstrual period.
Pregnancy and Childbirth
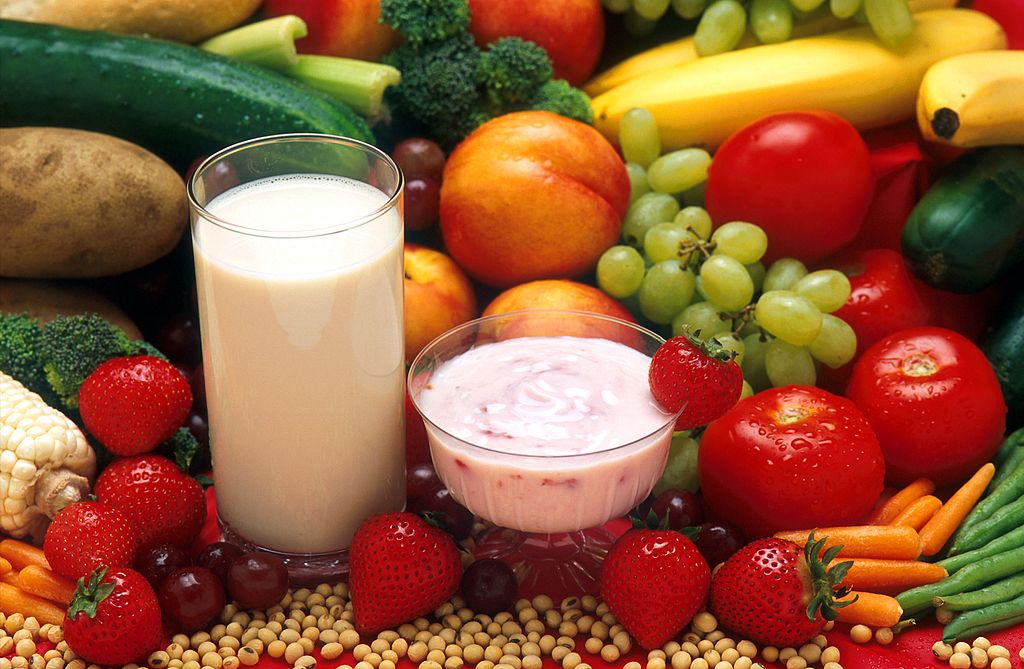
Pregnancy is the carrying of one or more offspring from fertilization until birth. This is one of the major functions of the female reproductive system. It involves virtually every other body system including the cardiovascular, urinary, and respiratory systems, to name just three. The maternal organism plays a critical role in the development of the offspring. She must provide all the nutrients and other substances needed for normal growth and development of the offspring, and she must also remove the wastes excreted by the offspring. Most nutrients are needed in greater amounts by a pregnant woman to meet fetal needs, but some are especially important, including folic acid, calcium, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids. A healthy diet (see photo in Figure 18.7.4), along with prenatal vitamin supplements, is recommended for the best pregnancy outcome. A pregnant woman should also avoid ingesting substances (such as alcohol) that can damage the developing offspring, especially early in the pregnancy when all of the major organs and organ systems are forming.

Trimesters of Pregnancy
When counted from the first day of the last menstrual period, the average duration of pregnancy is about 40 weeks (38 weeks when counted from the time of fertilization), but a pregnancy that lasts between 37 and 42 weeks is still considered within the normal range. From the point of view of the maternal organism, the total duration of pregnancy is typically divided into three periods, called trimesters, each of which lasts about three months. This division of the total period of gestation is useful for summarizing the typical changes a woman can expect during pregnancy. From the point of view of the developing offspring, however, the major divisions are different. They are the embryonic and fetal stages. The offspring is called an embryo from the time it implants in the uterus through the first eight weeks of life. After that, it is called a fetus for the duration of the pregnancy.
First Trimester
The first trimester begins at the time of fertilization and lasts for the next 12 weeks. Even before she knows she is pregnant, a woman in the first trimester is likely to experience signs and symptoms of pregnancy. She may notice a missed menstrual period, and she may also experience tender breasts, increased appetite, and more frequent urination. Many women also experience nausea and vomiting in the first trimester. This is often called “morning sickness,” because it commonly occurs in the morning, but it may occur at any time of day. Some women may lose weight during the first trimester because of morning sickness.
Second Trimester
The second trimester occurs during weeks 13 to 28 of pregnancy. A pregnant woman may feel more energized during this trimester. If she experienced nausea and vomiting during the first trimester, these symptoms often subside during the second trimester. Weight gain starts occurring during this trimester, as well. By about week 20, the fetus is getting large enough that the mother can feel its movements. The photo in Figure 18.7.5 shows a pregnant woman at week 26, toward the end of the second trimester. (For comparison, the same woman is shown on the right at the end of the third trimester.)

Third Trimester
The third trimester occurs during weeks 29 through birth (at about 40 weeks). During this trimester, the uterus expands rapidly, making up a larger and larger portion of the woman’s abdomen. Weight gain is also more rapid. During the third trimester, the movements of the fetus become stronger and more frequent, and they may become disruptive to the mother. As the fetus grows larger, its weight and the space it takes up may lead to symptoms in the mother such as back pain, swelling of the lower extremities, more frequent urination, varicose veins, and heartburn. By the end of the third trimester, the woman’s abdomen often will transform in shape as it drops, due to the fetus turning to a downward position before birth so its head rests on the cervix. This relieves pressure on the upper abdomen, but reduces bladder capacity and increases pressure on the pelvic floor and rectum.
Childbirth
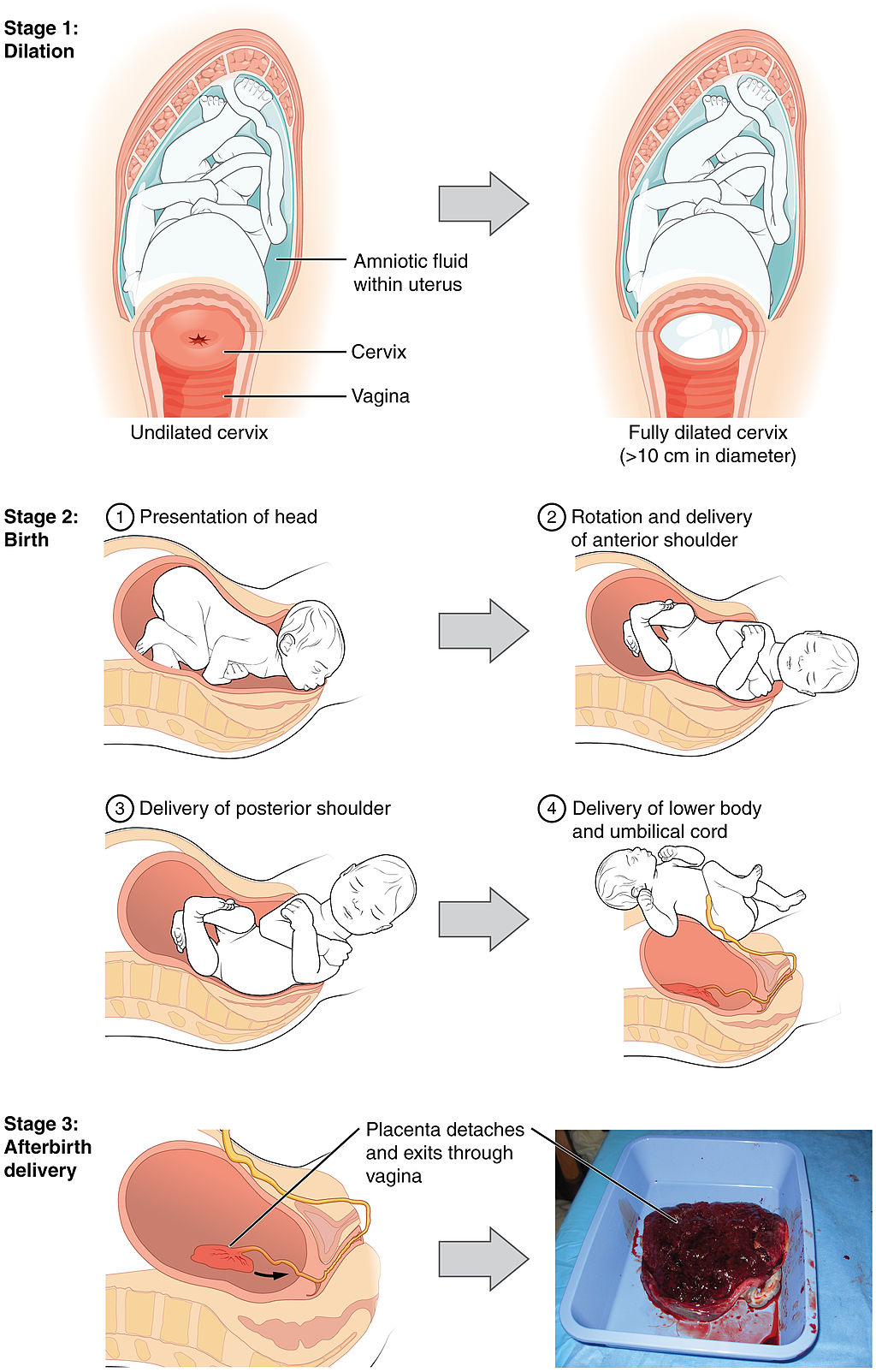
Near the time of birth, the amniotic sac — a fluid-filled membrane that encloses the fetus within the uterus — breaks in a gush of fluid. This is commonly called “breaking water.” Labour usually begins within a day of this event, although it may begin prior to it. Labour is the general term for the process of childbirth in which regular uterine contractions push the fetus and placenta out of the body. Labour can be divided into three stages, which are illustrated in Figure 18.7.6: dilation, birth, and afterbirth.
- During the dilation stage of labour, uterine contractions begin and become increasingly frequent and intense. The contractions push the baby’s head (most often) against the cervix, causing the cervical canal to dilate, or become wider. This lasts until the cervical canal has dilated to about 10 cm (almost 4 in.) in width, which may take 12 to 20 hours — or even longer. The cervical canal must be dilated to this extent in order for the baby’s head to fit through it.
- During birth, the baby descends (usually headfirst) through the cervical canal and vagina, and into the world outside. This is the stage when the mother generally starts bearing down during the contractions to help push out the fetus. This stage may last from about 20 minutes to two hours or more. Usually, within a minute or less of birth, the umbilical cord is cut, so the baby is no longer connected to the placenta.
- During the afterbirth stage, the placenta is delivered. This stage may last from a few minutes to a half hour.
Breastfeeding
Although the breasts are not classified as organs of the reproductive system, they nonetheless may play an important role in reproduction. The physiological function of the female breast is lactation, or the production of breast milk to feed an infant. This function is illustrated in Figure 18.7.7. Besides nutrients, breast milk provides hormones, antibodies, and other substances that help ensure a healthy start after birth.
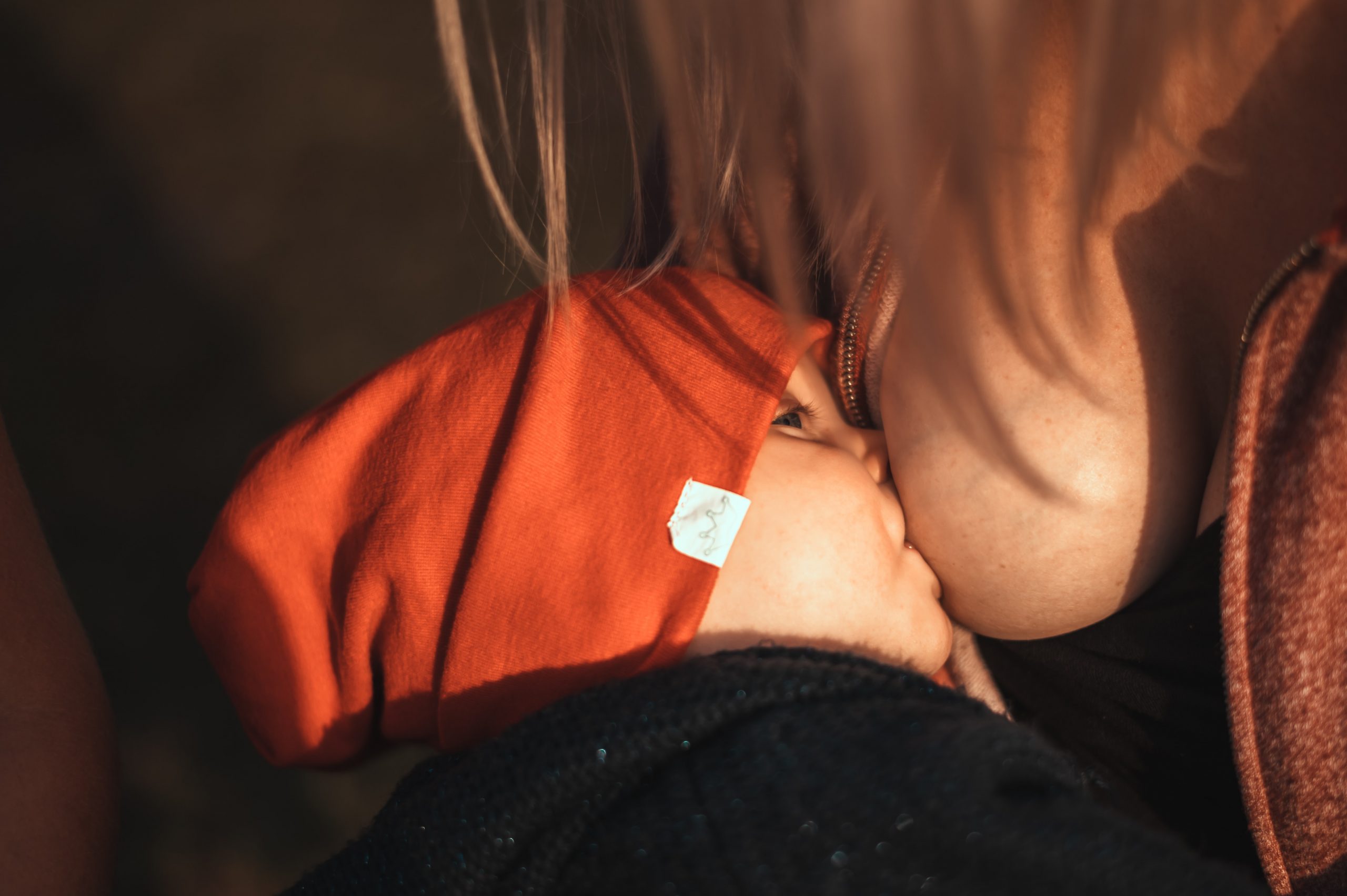

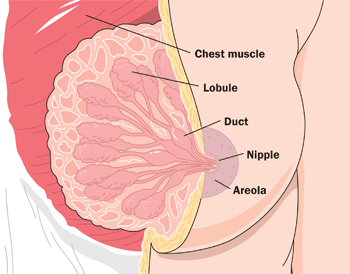
The Figure 18.7.7 (above) shows the correct way for an infant to suck the breast to stimulate the letdown of milk from the mammary glands (lips flanged, baby’s mouth on the nipple symmetrically). The letdown of milk when an infant sucks at the breast is one of the few examples of a positive feedback loop in the human organism. Sucking causes a release from the posterior pituitary gland of the hypothalamic hormone oxytocin. Oxytocin, in turn, causes milk to flow from the alveoli in the breasts where milk is produced, through the milk ducts, and into the milk sacs behind the areola. You can trace this route of milk through the breast in Figure 18.7.8. The baby can suck the milk out of the sacs through the nipple, where they converge. The release of milk stimulates the baby to continue sucking, which in turn keeps the milk flowing. Oxytocin is also an important hormone for maternal-child attachment.
Female Sex Hormones
Female reproduction could not occur without sex hormones released by the ovaries. These hormones include estrogen and progesterone.
Estrogen
Before birth, estrogen is released by the gonads in female fetuses and leads to the development of female reproductive organs. At puberty, estrogen levels rise and are responsible for sexual maturation, and for the development of female secondary sex characteristics (such as breasts). Estrogen is also needed to help regulate the menstrual cycle and ovulation throughout a woman’s reproductive years. Estrogen is produced primarily by follicular cells in the ovaries. During pregnancy, estrogen is also produced by the placenta. There are actually three forms of estrogen in the human female: estradiol, estriol, and estrone.
- Estradiol is the predominant form of estrogen during the reproductive years. It is also the most potent form of estrogen.
- Estriol is the predominant form of estrogen during pregnancy. It is also the weakest form of estrogen.
- Estrone is the predominant form of estrogen in post-menopausal women. It is intermediate in strength between the other two forms of estrogen.
Progesterone
Progesterone stands for “pro-gestational hormone.” It is synthesized and secreted primarily by the corpus luteum in the ovary. Progesterone plays many physiological roles, but is best known for its role during pregnancy. In fact, it is sometimes called the “hormone of pregnancy.” Among other functions, progesterone prepares the uterus for pregnancy each month by building up the uterine lining. If a pregnancy occurs, progesterone helps maintain the pregnancy in a number of ways, such as decreasing the maternal immune response to the genetically different embryo, and decreasing the ability of uterine muscle tissue to contract. Progesterone also prepares the mammary glands for lactation during pregnancy, and withdrawal of progesterone after birth is one of the triggers of milk production.
Feature: Myth vs. Reality
There are many myths associated with pregnancy. Most are harmless, but some may put the pregnant woman or fetus at risk. As always, knowledge is power.
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| “You should avoid petting your cat during pregnancy.” | Cat feces may be contaminated with microscopic parasites that can cause a disease called toxoplasmosis. Pregnant women who contract this disease are at risk of stillbirth, miscarriage, or giving birth to an infant with serious health problems. Pregnant women should not have contact with a cat’s litter box or feces, but petting a cat poses no real risk of infection. |
| “You should not dye your hair during pregnancy, because the chemicals can harm the fetus.” | Whereas some chemicals (such as certain pesticides) have been shown to be associated with birth defects, there is no evidence that using hair dye during pregnancy increases this risk. |
| “A pregnant woman needs to eat for two, so she should double her pre-pregnancy caloric intake.” | Throughout a typical pregnancy, a woman needs only about 300 extra calories per day, on average, to support her growing fetus. Most of the extra calories are needed during the last trimester, when the fetus is growing most rapidly. Doubling her caloric intake during pregnancy is likely to cause too much weight gain, which can be detrimental to her baby. Babies that weigh much more than the average 7.5 pounds (3.4 kg) at birth are more likely to develop diabetes and obesity in later life. |
| “Women who are pregnant have strange food cravings, such as ice cream with pickles.” | Some women do have food cravings during pregnancy, but they are not necessarily cravings for strange foods or unusual food combinations. For example, a pregnant woman might crave starchy foods for a few weeks, or she may be put off by certain foods that she loved before pregnancy. |
| “A pregnant woman has skin that glows.” | Pregnancy can actually be hard on the skin and its appearance. Besides stretch marks on the abdomen and breasts, pregnancy may lead to spider veins, varicose veins, new freckles, darkening of moles, and acne flare-ups. In addition, as many as 75 per cent of pregnant women experience chloasma, which is the emergence of blotchy brown patches of skin on the face due to high estrogen levels. Chloasma is often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy.” |
18.7 Summary
- Oogenesis is the process of producing ova in the ovaries of a female fetus. Oogenesis begins when a diploid oogonium divides by mitosis to produce a diploid primary oocyte. The primary oocyte begins meiosis I and then remains at this stage in an immature ovarian follicle until after birth. By birth, a female’s ovaries contain all the eggs she will ever produce, numbering at least a million.
- After puberty, one follicle a month matures, and its primary oocyte completes meiosis I to produce a secondary oocyte, which begins meiosis II. During ovulation, the mature follicle bursts open, and the secondary oocyte leaves the ovary and enters an oviduct.
- While a follicle is maturing in an ovary each month, the endometrium in the uterus is building up to prepare for an embryo. Around the time of ovulation, cervical mucus becomes thinner and more alkaline to help sperm reach the secondary oocyte.
- If the secondary oocyte is fertilized by a sperm, it quickly completes meiosis II and forms a diploid zygote, which will continue through the oviduct. The zygote will go through multiple cell divisions before reaching and implanting in the uterus. If the secondary oocyte is not fertilized, it will not complete meiosis II, and it will soon disintegrate.
- Pregnancy is the carrying of one or more offspring from fertilization until birth. The maternal organism must provide all the nutrients and other substances needed by the developing offspring, and also remove its wastes. She should also avoid exposures that could potentially damage the offspring, especially early in the pregnancy when organ systems are developing.
- The average duration of pregnancy is 40 weeks (from the first day of the last menstrual period) and is divided into three trimesters of about three months each. Each trimester is associated with certain events and conditions that a pregnant woman may expect, such as morning sickness during the first trimester, feeling fetal movements for the first time during the second trimester, and rapid weight gain in both fetus and mother during the third trimester.
- Labour, which is the general term for the birth process, usually begins around the time the amniotic sac breaks and its fluid leaks out. Labour occurs in three stages: dilation of the cervix, birth of the baby, and delivery of the placenta (afterbirth).
- The physiological function of female breasts is lactation, or the production of breast milk to feed an infant. Sucking on the breast by the infant stimulates the release of the hypothalamic hormone oxytocin from the posterior pituitary, which causes the flow of milk. The release of milk stimulates the baby to continue sucking, which in turn keeps the milk flowing. This is one of the few examples of positive feedback in the human organism.
- The ovaries produce female sex hormones, including estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen is responsible for sexual differentiation before birth, as well as for sexual maturation and the development of secondary sex characteristics at puberty. It is also needed to help regulate the menstrual cycle and ovulation after puberty and until menopause. Progesterone prepares the uterus for pregnancy each month during the menstrual cycle, and helps maintain the pregnancy if fertilization occurs.
18.7 Review Questions
-
- What is pregnancy, and what is the role of the maternal organism in pregnancy?
- What is the average duration of pregnancy? Identify the trimesters of pregnancy.
- Define labour. What event is often a sign that labour will soon begin?
- Identify the stages of labour.
- Describe the physiological function of female breasts. How is this function controlled?
- Identify the functions of the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone.
- Describe the roles of the cervix in fertilization and childbirth.
18.7 Explore More
Pregnancy 101 | National Geographic, 2018.
How do pregnancy tests work? – Tien Nguyen, TED-Ed, 2015.
Fertilization, Nucleus Medical Media, 2013.
The science of milk – Jonathan J. O’Sullivan, TED-Ed, 2017.
Attributions
Figure 18.7.1
Pregnant by Mustafa Omar on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 18.7.2
Oogenesis by Acedatrey2 on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) license.
Figure 18.7.3
Blausen_0404_Fertilization by BruceBlaus on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en) license.
Figure 18.7.4
Prenatal Diet/ Milch-Jogurt-Früchte by Peggy Greb, Agricultural Research Service (USDA) on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 18.7.5
Pregnancy_comparison by Maustrauser at English Wikipedia on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 18.7.6
Stages_of_Childbirth-02 by OpenStax on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) license.
Figure 18.7.7
Childhood: breast feeding [photo] by Jan Kopřiva on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 18.7.8
Breast-Diagram by Women’s Health (NCI/ NIH) on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
References
Betts, J. G., Young, K.A., Wise, J.A., Johnson, E., Poe, B., Kruse, D.H., Korol, O., Johnson, J.E., Womble, M., DeSaix, P. (2013, June 19). Figure 28.21 Stages of childbirth [digital image]. In Anatomy and Physiology (Section 28.4). OpenStax. https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/28-4-maternal-changes-during-pregnancy-labor-and-birth
Blausen.com Staff. (2014). Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436
National Geographic. (2018, December 20). Pregnancy 101 | National Geographic. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XEfnq4Q4bfk&feature=youtu.be
Nucleus Medical Media. (2013, January 31). Fertilization. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_5OvgQW6FG4&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed, (2015, July 7). How do pregnancy tests work? – Tien Nguyen. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aOfWTscU8YM&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2017, January 31). The science of milk – Jonathan J. O’Sullivan. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xmNzUEmFZMg&feature=youtu.be
A mature haploid male or female germ cell which is able to unite with another of the opposite sex in sexual reproduction to form a zygote.
The female sex hormone secreted mainly by the ovaries.
The fusion of haploid gametes, egg and sperm, to form the diploid zygote.
An unborn offspring of a mammal, in particular an unborn human baby more than eight weeks after conception.
The male reproductive cell.
A pair of female reproductive organs that produces eggs and secretes estrogen.
The gamete produced by a female.
A period during which humans become sexually mature.
The cessation of a woman’s menstrual cycles, usually by age 52.
The production or development of an ovum.
The term used when a cell has half the usual number of chromosomes.
A diploid stem cell in an ovary that undergoes mitosis to begin the process of oogenesis.
A part of the cell cycle when replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei and then subsequent cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the number of chromosomes is maintained.
Describes a cell that contain two copies of each chromosome.
A cell in an ovary which may undergo meiotic division to form an ovum.
A special type of cell division in sexually-reproducing organisms used to produce the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells with only one copy of each chromosome.
The functional unit of an ovary that consists of a nest of epithelial cells surrounding an egg.
The release of a secondary oocyte from an ovary about half way through the menstrual cycle.
An ovarian structure that forms from a follicle after it matures and ovulates an egg.
Small, fingerlike projections at the end of the oviducts, through which eggs move from the ovaries to the uterus. The fimbriae are connected to the ovary.
The female reproductive organ in which first an embryo and then a fetus grows and develops until birth.
The innermost layer of the uterus that builds up during each menstrual cycle and helps nourish the embryo if fertilization occurs or is shed from the uterus as menstrual flow if fertilization does not occur.
The neck of the uterus that protrudes down into the vagina and through which a canal connects the vagina and uterus.
The female reproductive organ that receives sperm during sexual intercourse and provides a passageway for a baby to leave the mother’s body during birth.
The union of the sperm cell and the egg cell. Also known as a fertilized ovum, the zygote begins as a single cell but divides rapidly in the days following fertilization. After this two-week period of cell division, the zygote eventually becomes an embryo.
A fluid-filled ball of cells that develops a few days after fertilization in the process of blastulation.
The carrying of one or more offspring from fertilization until birth.
One of three, approximately three-month periods into which a pregnancy is divided.
A stage of growth and development that occurs from implantation in the uterus through the eighth week after fertilization.
The fluid-filled sac that contains and protects a fetus in the womb.
A general term for the process of childbirth, which includes three stages: dilation of the cervical canal, birth of the child, and delivery of the placenta (afterbirth).
Refers to the front of the chest or, more specifically, to the mammary gland. The mammary gland is a milk producing gland. It is composed largely of fat.
The production of breastmilk to feed an infant.
A control mechanism that serves to intensify a response until an endpoint is reached.
The master gland of the endocrine system that secretes many hormones, the majority of which regulate other endocrine glands.
An endocrine hormone secreted by the pituitary gland that controls a variety of functions, including during childbirth to stimulate uterine contractions and during lactation to trigger milk letdown.
The monthly cycle of processes and events in the ovaries and uterus of a sexually mature human female until menopause.
A temporary organ that consists of a large mass of maternal and fetal blood vessels through which the mother’s and embryo’s or fetus’s blood exchange substances.
The female sex hormone secreted mainly by the ovaries that helps maintain a successful pregnancy.
An exocrine gland in humans and other mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word mamma, "breast".
One of two female reproductive organs that carry eggs from an ovary to the uterus and are the site where fertilization usually takes place.
A trait that is different in males and females but is not directly involved in reproduction, such as male facial hair and female breasts.

