18.8 Menstrual Cycle
Created by CK-12 Foundation/Adapted by Christine Miller

Taboo Topic
The banner in Figure 18.8.1 was carried in a 2014 march in Uganda as part of the celebration of Menstrual Hygiene Day. Menstrual Hygiene Day is an awareness day on May 28 of each year that aims to raise awareness worldwide about menstruation and menstrual hygiene. Maintaining good menstrual hygiene is difficult in developing countries like Uganda because of taboos on discussing menstruation and lack of availability of menstrual hygiene products. Poor menstrual hygiene, in turn, can lead to embarrassment, degradation, and reproductive health problems in females. May 28 was chosen as Menstrual Hygiene Day because of its symbolism. May is the fifth month of the year, and most women average five days of menstrual bleeding each month. The 28th day was chosen because the menstrual cycle averages about 28 days.
What Is the Menstrual Cycle?
The menstrual cycle refers to natural changes that occur in the female reproductive system each month during the reproductive years. The cycle is necessary for the production of ova and the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. It involves changes in both the ovaries and the uterus, and is controlled by pituitary and ovarian hormones. Day 1 of the cycle is the first day of the menstrual period, when bleeding from the uterus begins as the built-up endometrium lining the uterus is shed. The endometrium builds up again during the remainder of the cycle, only to be shed again during the beginning of the next cycle if pregnancy does not occur. In the ovaries, the menstrual cycle includes the development of a follicle, ovulation of a secondary oocyte, and then degeneration of the follicle if pregnancy does not occur. Both uterine and ovarian changes during the menstrual cycle are generally divided into three phases, although the phases are not the same in the two organs.
Menarche and Menopause
The female reproductive years are delineated by the start and stop of the menstrual cycle. The first menstrual period usually occurs around 12 or 13 years of age, an event that is known as menarche. There is considerable variation among individuals in the age at menarche. It may occasionally occur as early as eight years of age or as late as 16 years of age and still be considered normal. The average age is generally later in the developing world, and earlier in the developed world. This variation is thought to be largely attributable to nutritional differences.
The cessation of menstrual cycles at the end of a woman’s reproductive years is termed menopause. The average age of menopause is 52 years, but it may occur normally at any age between about 45 and 55 years of age. The age of menopause varies due to a variety of biological and environmental factors. It may occur earlier as a result of certain illnesses or medical treatments.
Variation in the Menstrual Cycle
The length of the menstrual cycle — as well as its phases — may vary considerably, not only among different women, but also from month to month for a given woman. The average length of time between the first day of one menstrual period and the first day of the next menstrual period is 28 days, but it may range from 21 days to 45 days. Cycles are considered regular when a woman’s longest and shortest cycles differ by less than eight days. The menstrual period itself is usually about five days long, but it may vary in length from about two days to seven days.
Ovarian Cycle
The events of the menstrual cycle that take place in the ovaries make up the ovarian cycle. It consists of changes that occur in the follicles of one of the ovaries. The ovarian cycle is divided into the following three phases: follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase. These phases are illustrated in Figure 18.8.2.
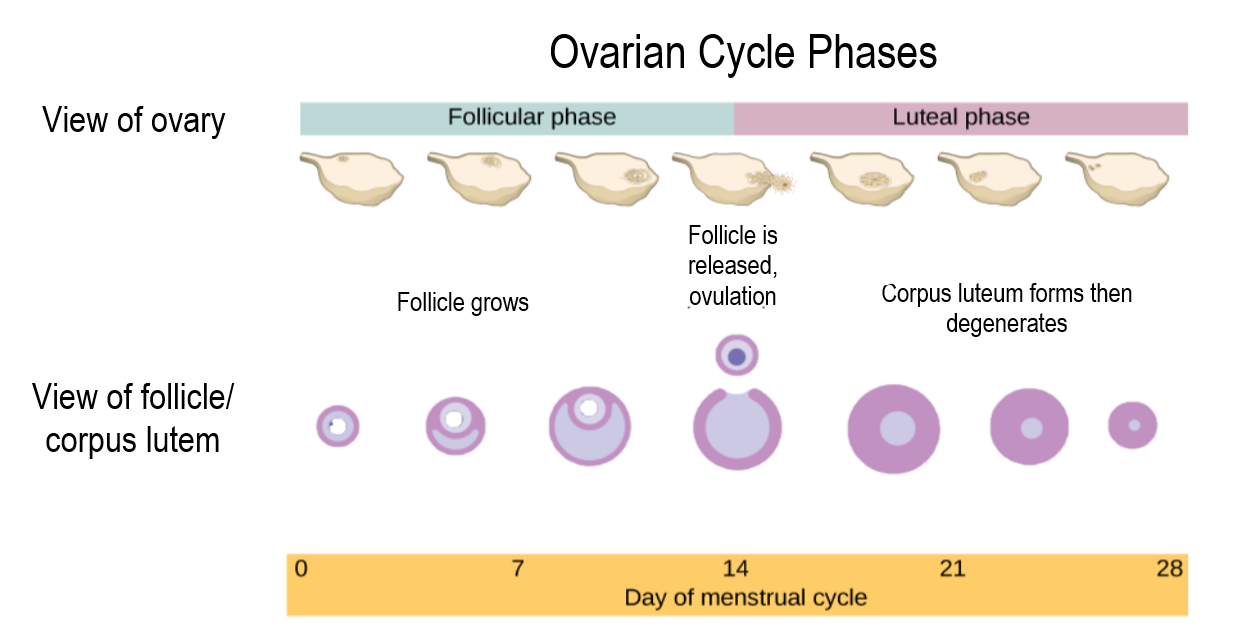
Follicular Phase
The follicular phase is the first phase of the ovarian cycle. It generally lasts about 12 to 14 days for a 28-day menstrual cycle. During this phase, several ovarian follicles are stimulated to begin maturing, but usually only one — called the Graafian follicle — matures completely so it is ready to release an egg. The other maturing follicles stop growing and disintegrate. Follicular development occurs because of a rise in the blood level of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), which is secreted by the pituitary gland. The maturing follicle releases estrogen, the level of which rises throughout the follicular phase. You can see these and other changes in hormone levels that occur during the menstrual cycle in the following chart.
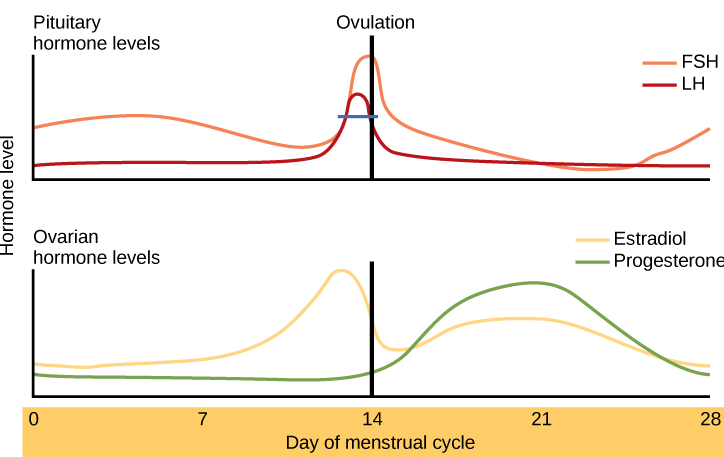
Ovulation
Ovulation is the second phase of the ovarian cycle. It usually occurs around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle. During this phase, the Graafian follicle ruptures and releases its ovum. Ovulation is stimulated by a sudden rise in the blood level of luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary gland. This is called the LH surge. You can see the LH surge in the top hormone graph in Figure 18.8.3. The LH surge generally starts around day 12 of the cycle and lasts for a day or two. The surge in LH is triggered by a continued rise in estrogen from the maturing follicle in the ovary. During the follicular phase, the rising estrogen level actually suppresses LH secretion by the pituitary gland. However, by the time the follicular phase is nearing its end, the level of estrogen reaches a threshold level above which this effect is reversed, and estrogen stimulates the release of a large amount of LH. The surge in LH matures the ovum and weakens the wall of the follicle, causing the fully developed follicle to release its secondary oocyte.
Luteal Phase
The luteal phase is the third and final phase of the ovarian cycle. It typically lasts about 14 days in a 28-day menstrual cycle. At the beginning of the luteal phase, FSH and LH cause the Graafian follicle that ovulated the egg to transform into a structure called a corpus luteum. The corpus luteum secretes progesterone, which in turn suppresses FSH and LH production by the pituitary gland and stimulates the continued buildup of the endometrium in the uterus. How this phase ends depends on whether or not the ovum has been fertilized.
- If fertilization has not occurred, the falling levels of FSH and LH during the luteal phase cause the corpus luteum to atrophy, so its production of progesterone declines. Without a high level of progesterone to maintain it, the endometrium starts to break down. By the end of the luteal phase, the endometrium can no longer be maintained, and the next menstrual cycle begins with the shedding of the endometrium (menses).
- If fertilization has occurred so a zygote forms and then divides to become a blastocyst, the outer layer of the blastocyst produces a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). This hormone is very similar to LH and preserves the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum can then continue to secrete progesterone to maintain the new pregnancy.
Uterine Cycle
The events of the menstrual cycle that take place in the uterus make up the uterine cycle. This cycle consists of changes that occur mainly in the endometrium, which is the layer of tissue that lines the uterus. The uterine cycle is divided into the following three phases: menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase. These phases are illustrated in Figure 18.8.4.
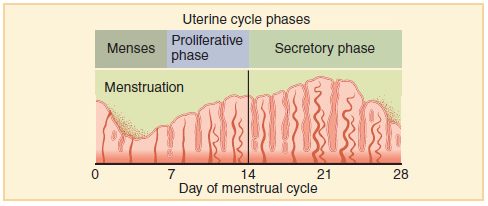
Menstruation
Menstruation (also called menstrual period or menses) is the first phase of the uterine cycle. It occurs if fertilization has not taken place during the preceding menstrual cycle. During menstruation, the endometrium of the uterus, which has built up during the preceding cycle, degenerates and is shed from the uterus, flowing through an opening in the cervix, and out through the external opening of the vagina. The average loss of blood during menstruation is about 35 mL (about 1 oz or 2 tablespoons). The flow of blood is often accompanied by uterine cramps, which may be severe in some women.
Proliferative Phase
The proliferative phase is the second phase of the uterine cycle. During this phase, estrogen secreted by cells of the maturing ovarian follicle causes the lining of the uterus to grow, or proliferate. Estrogen also stimulates the cervix of the uterus to secrete larger amounts of thinner mucus that can help sperm swim through the cervix and into the uterus, making fertilization more likely.
Secretory Phase
The secretory phase is the third and final phase of the uterine cycle. During this phase, progesterone produced by the corpus luteum in the ovary stimulates further changes in the endometrium so it is more receptive to implantation of a blastocyst. For example, progesterone increases blood flow to the uterus and promotes uterine secretions. It also decreases the contractility of smooth muscle tissue in the uterine wall.
Bringing it All Together
It is important to note that the pituitary gland, the ovaries and the uterus are all responsible for parts of the ovarian and uterine cycles. The pituitary hormones, LH and FSH affect the ovarian cycle and its hormones. The ovarian hormones, estrogen and progesterone affect the uterine cycle and also feedback on the pituitary gland. Look at Figure 18.8.5 and look at what is happening on different days of the cycle in each of the sets of hormones, the ovarian cycle and the uterine cycle.
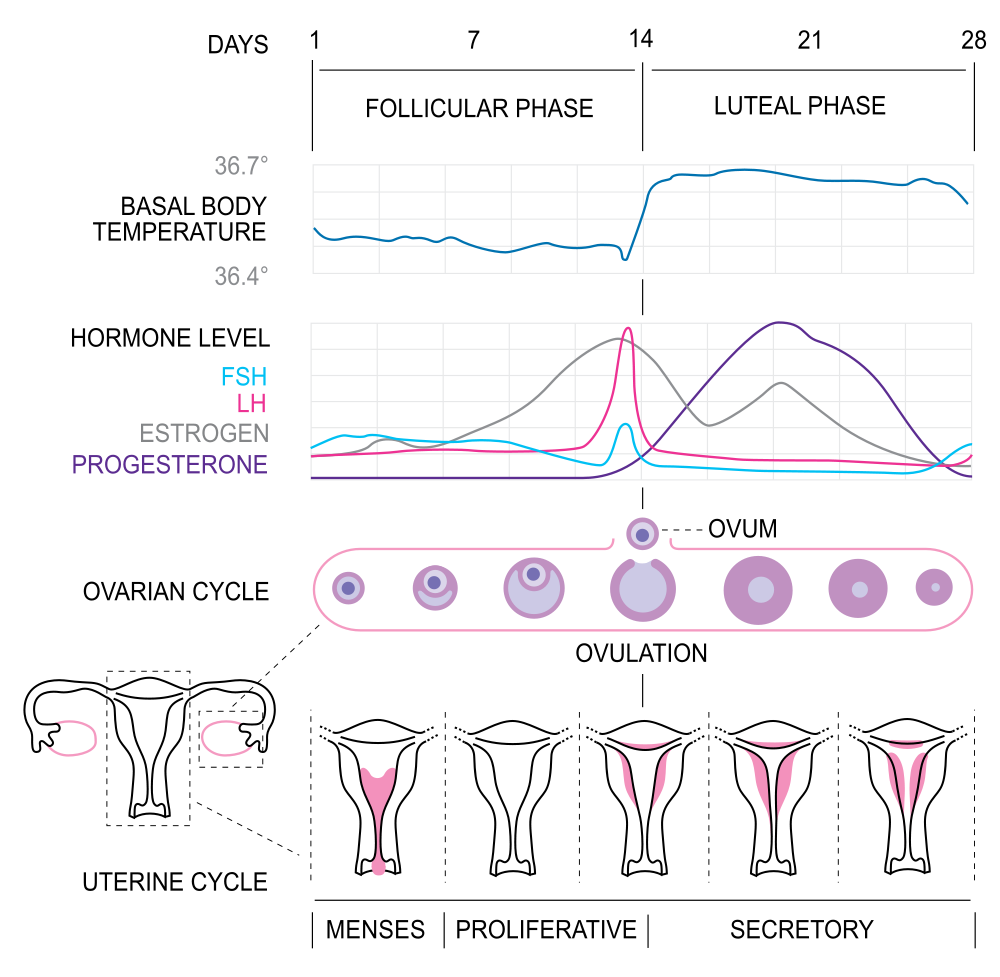
18.8 Summary
- The menstrual cycle refers to natural changes that occur in the female reproductive system each month during the reproductive years, except when a woman is pregnant. The cycle is necessary for the production of ova and the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. It involves changes in both the ovaries and uterus, and is controlled by pituitary gland hormones (FSH and LH) and ovarian hormones (estrogen and progesterone).
- The female reproductive period is delineated by menarche, or the first menstrual period, which usually occurs around age 12 or 13; and by menopause, or the cessation of menstrual periods, which typically occurs around age 52. A typical menstrual cycle averages 28 days in length but may vary normally from 21 to 45 days. The average menstrual period is five days long, but may vary normally from two to seven days. These variations in the menstrual cycle may occur both between women and within individual women from month to month.
- The events of the menstrual cycle that take place in the ovaries make up the ovarian cycle. It includes the follicular phase (when a follicle and its ovum mature due to rising levels of FSH), ovulation (when the ovum is released from the ovary due to a rise in estrogen and a surge in LH), and the luteal phase (when the follicle is transformed into a structure called a corpus luteum that secretes progesterone). In a 28-day menstrual cycle, the follicular and luteal phases typically average about two weeks in length, with ovulation generally occurring around day 14 of the cycle.
- The events of the menstrual cycle that take place in the uterus make up the uterine cycle. It includes menstruation, which generally occurs on days 1 to 5 of the cycle and involves shedding of endometrial tissue that built up during the preceding cycle; the proliferative phase, during which the endometrium builds up again until ovulation occurs; and the secretory phase, which follows ovulation and during which the endometrium secretes substances and undergoes other changes that prepare it to receive an embryo.
18.8 Review Questions
-
- What is the menstrual cycle? Why is the menstrual cycle necessary in order for pregnancy to occur?
- What organs are involved in the menstrual cycle?
- Identify the two major events that mark the beginning and end of the reproductive period in females. When do these events typically occur?
- Discuss the average length of the menstrual cycle and menstruation, as well as variations that are considered normal.
- If the LH surge did not occur in a menstrual cycle, what do you think would happen? Explain your answer.
- Give one reason why FSH and LH levels drop in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
18.8 Explore More
Why do women have periods? TED-Ed, 2015.
Girl’s Rite of Passage | National Geographic, 2007.
Attributions
Figure 18.8.1
WaterforPeople_Uganda by WaterforPeople_Uganda on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0) license.
Figure 18.8.2
Ovarian Cycle by CNX OpenStax on Wikimedia Commons is used and adapted under a CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0) license.
Figure 18.8.3
Figure_43_04_04 by CNX OpenStax on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0) license. (Original: modification of work by Mikael Häggström)
Figure 18.8.4
Ovarian and menstrual cycle by OpenStax College on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0) license.
Figure 18.8.5
1000px-MenstrualCycle2_en.svg by Isometrik on Wikimedia Common is used under a CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0) license.
References
Betts, J. G., Young, K.A., Wise, J.A., Johnson, E., Poe, B., Kruse, D.H., Korol, O., Johnson, J.E., Womble, M., DeSaix, P. (2013, June 19). Figure 27.15 Hormone levels in ovarian and menstrual cycles [digital image]. In Anatomy and Physiology (Section 27.2). OpenStax. https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/27-2-anatomy-and-physiology-of-the-female-reproductive-system
National Geographic. (2007, May 31). Girl’s rite of passage | National Geographic. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5B3Abpv0ysM&feature=youtu.be
OpenStax. (2016, May 27) Figure 4 Rising and falling hormone levels result in progression of the ovarian and menstrual cycles [digital image]. In Open Stax, Biology (Section 43.4). OpenStax CNX. https://cnx.org/contents/GFy_h8cu@10.53:Ha3dnFEx@6/Hormonal-Control-of-Human-Reproduction
TED-Ed. (2015, October 19). Why do women have periods? YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cjbgZwgdY7Q&feature=youtu.be
The monthly cycle of processes and events in the ovaries and uterus of a sexually mature human female until menopause.
The female reproductive organ in which first an embryo and then a fetus grows and develops until birth.
The carrying of one or more offspring from fertilization until birth.
The innermost layer of the uterus that builds up during each menstrual cycle and helps nourish the embryo if fertilization occurs or is shed from the uterus as menstrual flow if fertilization does not occur.
The functional unit of an ovary that consists of a nest of epithelial cells surrounding an egg.
The beginning of menstruation; first monthly period in a female.
The cessation of a woman’s menstrual cycles, usually by age 52.
The series of events of the menstrual cycle that occur in the ovaries, including maturation of a follicle, ovulation, and development of the corpus luteum.
A pair of female reproductive organs that produces eggs and secretes estrogen.
The phase of the ovarian cycle during which follicles in the ovary mature. It ends with ovulation. The main hormones controlling this stage are follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadotropin-releasing hormone.
A hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland which promotes the formation of ova or sperm.
The master gland of the endocrine system that secretes many hormones, the majority of which regulate other endocrine glands.
The female sex hormone secreted mainly by the ovaries.
The release of a secondary oocyte from an ovary about half way through the menstrual cycle.
A hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates ovulation in females and the synthesis of androgen in males.
A cell in an ovary which may undergo meiotic division to form an ovum.
The later phase of the ovarian cycle. It begins with the formation of the corpus luteum and ends in either pregnancy or degeneration of the corpus luteum.
A hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates ovulation in females and the synthesis of androgen in males.
An ovarian structure that forms from a follicle after it matures and ovulates an egg.
The female sex hormone secreted mainly by the ovaries that helps maintain a successful pregnancy.
The fusion of haploid gametes, egg and sperm, to form the diploid zygote.
The union of the sperm cell and the egg cell. Also known as a fertilized ovum, the zygote begins as a single cell but divides rapidly in the days following fertilization. After this two-week period of cell division, the zygote eventually becomes an embryo.
A fluid-filled ball of cells that develops a few days after fertilization in the process of blastulation.
Human chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone produced by cells that are surrounding a growing embryo, which eventually forms the placenta after implantation. The presence of hCG is detected in some pregnancy tests.
The events of the menstrual cycle that occur in the uterus, including menses and the buildup of the endometrium.
The process in which the endometrium of the uterus is shed from the body during the first several days of the menstrual cycle; also called monthly period or menses.
The second phase of the uterine cycle when estrogen causes the endometrium lining of the uterus to grow, or proliferate, during this time.
The neck of the uterus that protrudes down into the vagina and through which a canal connects the vagina and uterus.
The male reproductive cell.
The stage of the menstrual cycle immediately following ovulation, during which the womb lining is at full thickness and its mucus glands are actively secreting.
An involuntary, nonstriated muscle that is found in the walls of internal organs such as the stomach.
The gamete produced by a female.
A stage of growth and development that occurs from implantation in the uterus through the eighth week after fertilization.

