4.13 Mitosis and Cytokinesis
Created by: CK-12/Adapted by Christine Miller
Divide and Split
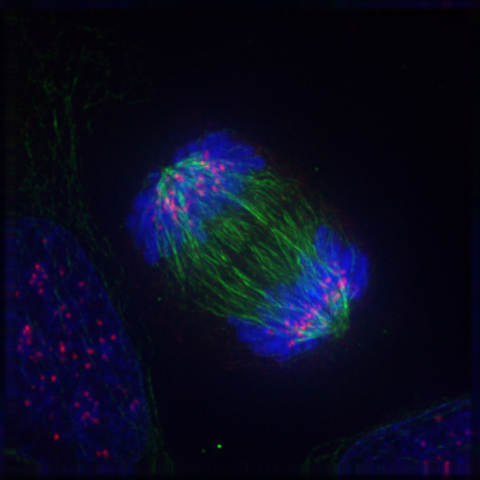
Can you guess what the colourful image in Figure 4.13.1 represents? It shows a eukaryotic cell during the process of cell division. In particular, the image shows the cell in a part of cell division called anaphase, where the DNA is being pulled to opposite ends of the cell. Normally, DNA is located in the nucleus of most human cells. The nucleus divides before the cell itself splits in two, and before the nucleus divides, the cell’s DNA is replicated (or copied). There must be two copies of the DNA so that each daughter cell will have a complete copy of the genetic material from the parent cell. How is the replicated DNA sorted and separated so that each daughter cell gets a complete set of the genetic material? To answer that question, you first need to know more about DNA and the forms it takes.
The Forms of DNA
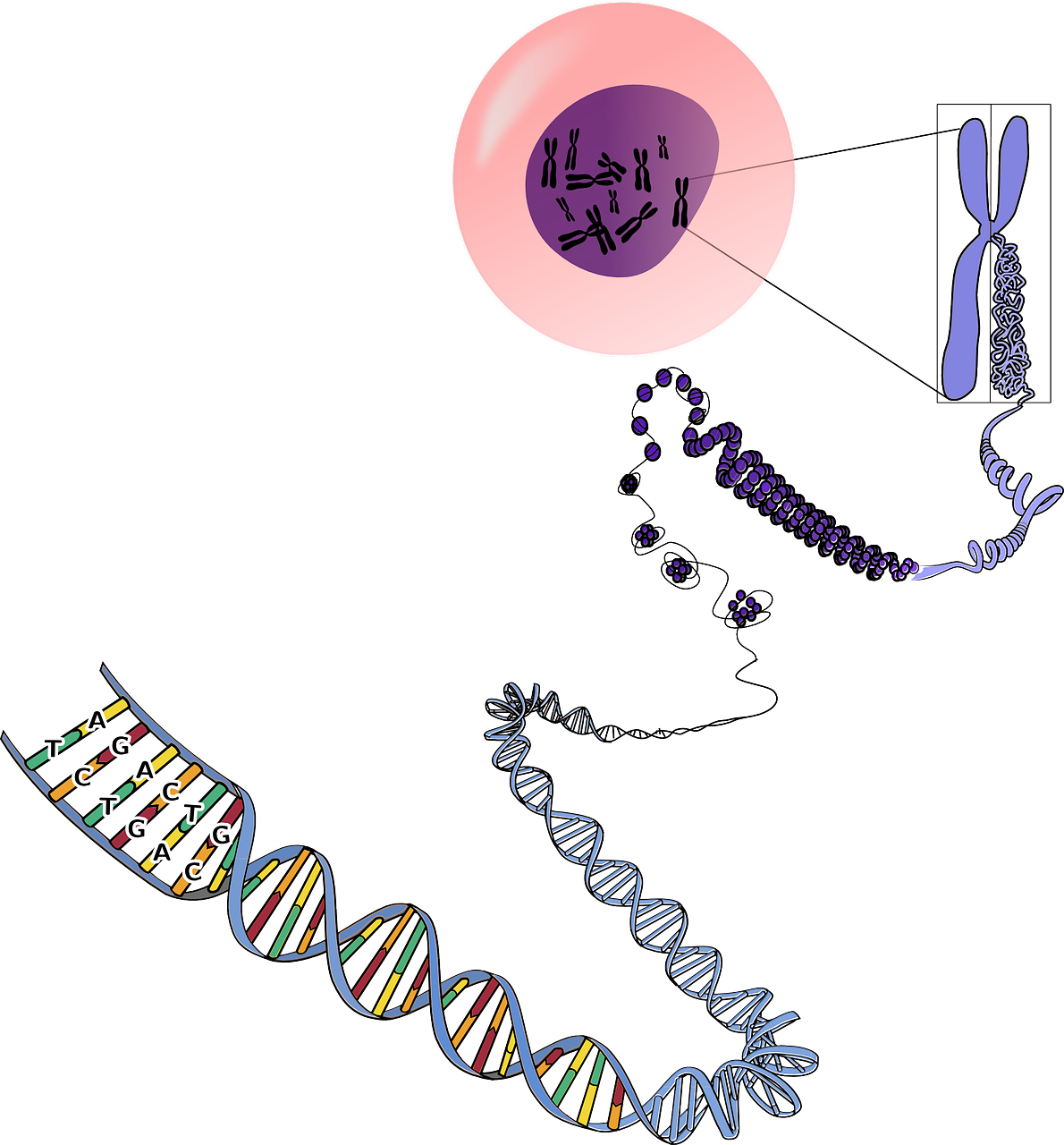
Except when a eukaryotic cell divides, its nuclear DNA exists as a grainy material called chromatin. Only once a cell is about to divide and its DNA has replicated does DNA condense and coil into the familiar X-shaped form of a chromosome, like the one shown below.
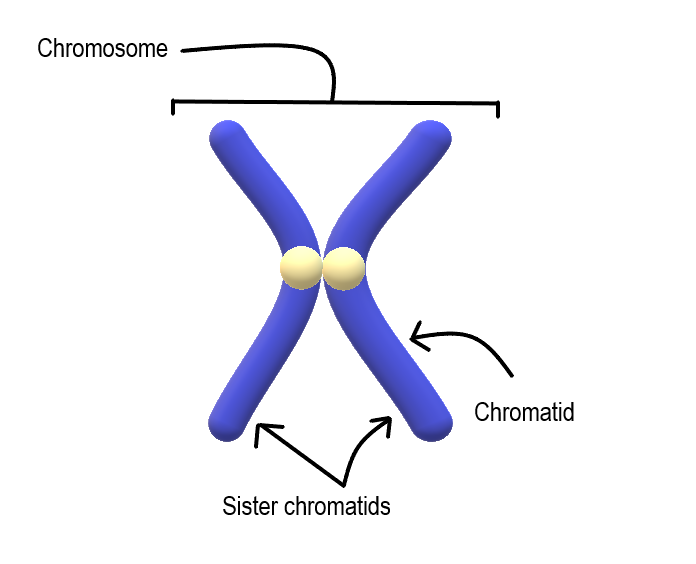
Most cells in the human body have two pairs of 23 different chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. Cells that have two pairs of chromosomes are called diploid. Because DNA has already replicated when it coils into a chromosome, each chromosome actually consists of two identical structures called sister chromatids. Sister chromatids are joined together at a region called a centromere.
Mitosis
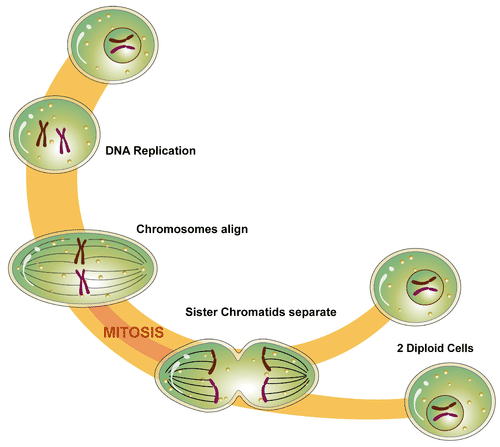
The process in which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides is called mitosis. During mitosis, the two sister chromatids that make up each chromosome separate from each other and move to opposite poles of the cell. This is shown in the figure below.
Mitosis actually occurs in four phases. The phases are called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
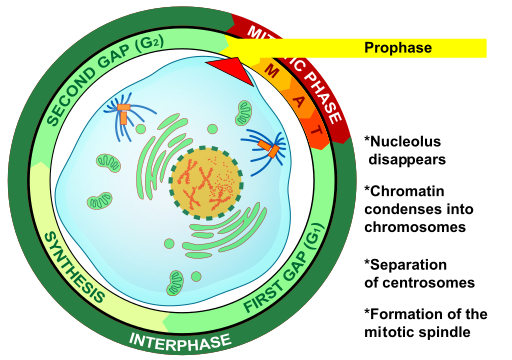
Prophase
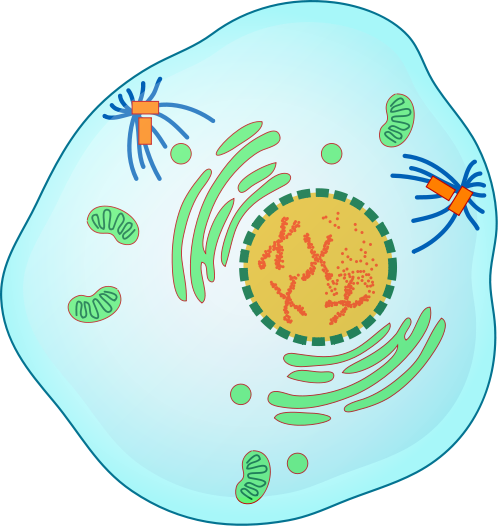
The first and longest phase of mitosis is prophase. During prophase, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope (the membrane surrounding the nucleus) breaks down. In animal cells, the centrioles near the nucleus begin to separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. Centrioles are small organelles found only in eukaryotic cells. They help ensure that the new cells that form after cell division each contain a complete set of chromosomes. As the centrioles move apart, a spindle starts to form between them. The spindle consists of fibres made of microtubules.
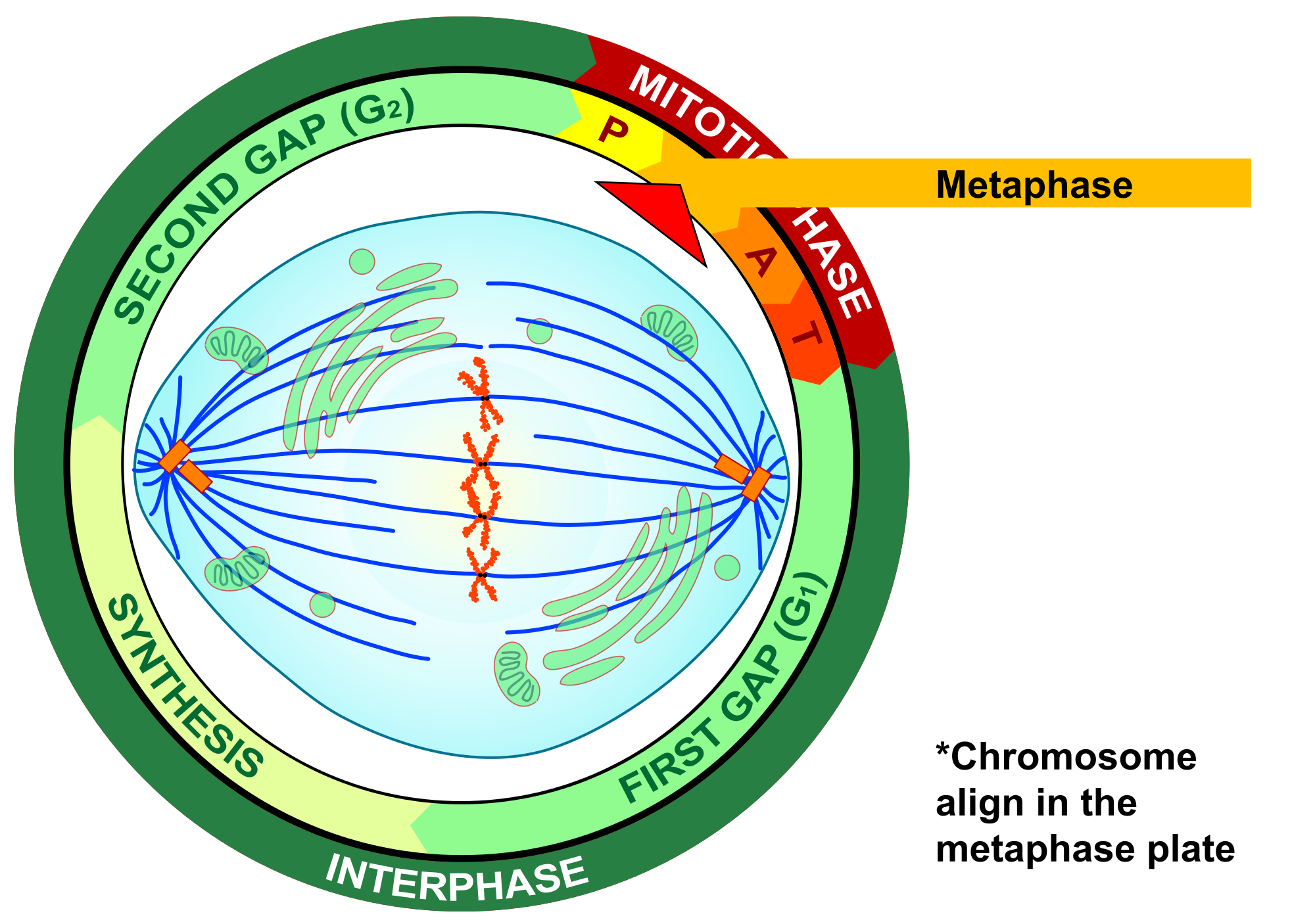
Metaphase
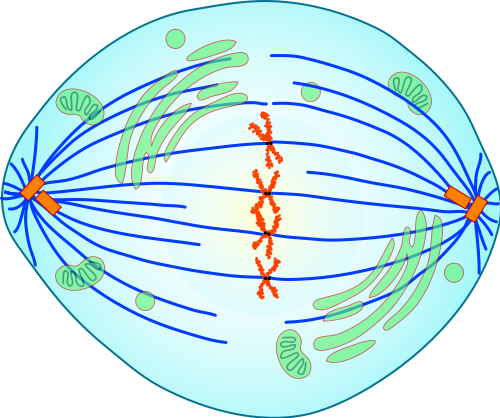
During metaphase, spindle fibres attach to the centromere of each pair of sister chromatids. As you can see in Figure 4.13.7, the sister chromatids line up at the equator (or center) of the cell. The spindle fibres ensure that sister chromatids will separate and go to different daughter cells when the cell divides.
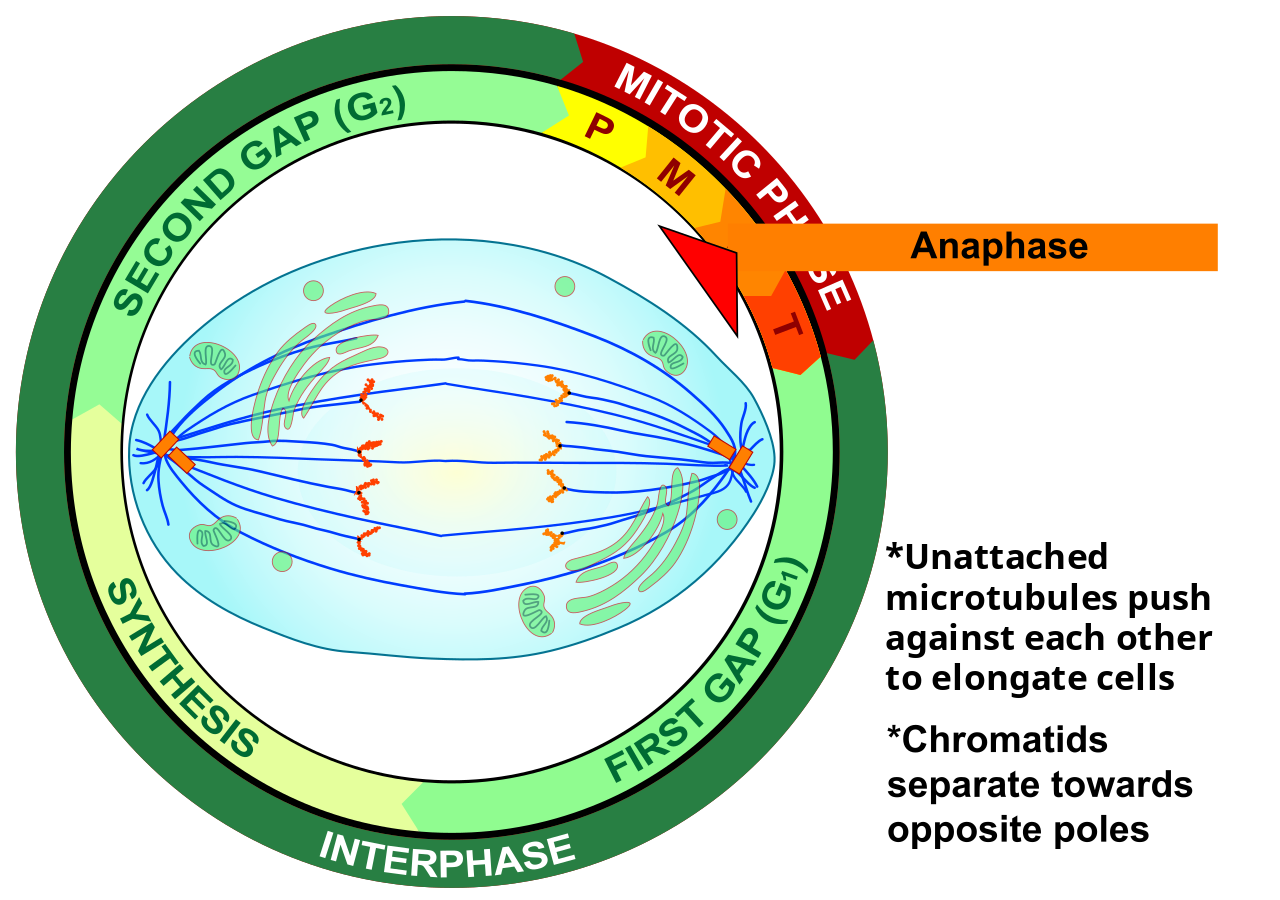
Anaphase
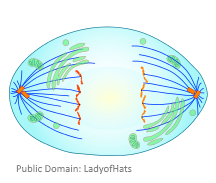
During anaphase, sister chromatids separate and the centromeres divide. The sister chromatids are pulled apart by the shortening of the spindle fibres. This is a little like reeling in a fish by shortening the fishing line. One sister chromatid moves to one pole of the cell, and the other sister chromatid moves to the opposite pole. At the end of anaphase, each pole of the cell has a complete set of chromosomes.
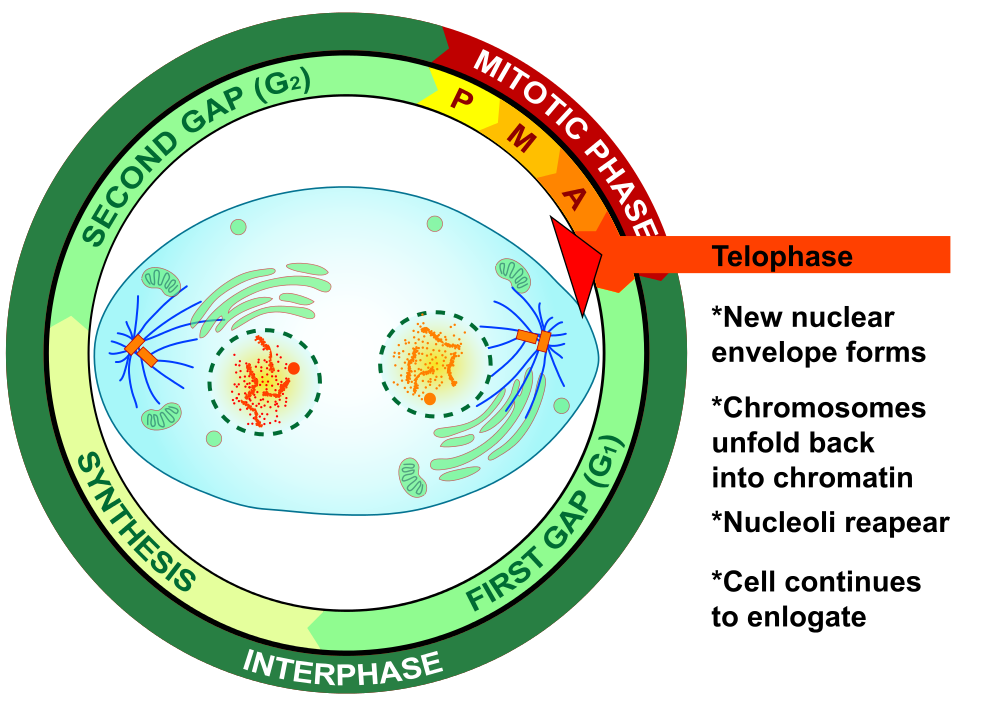
Telophase
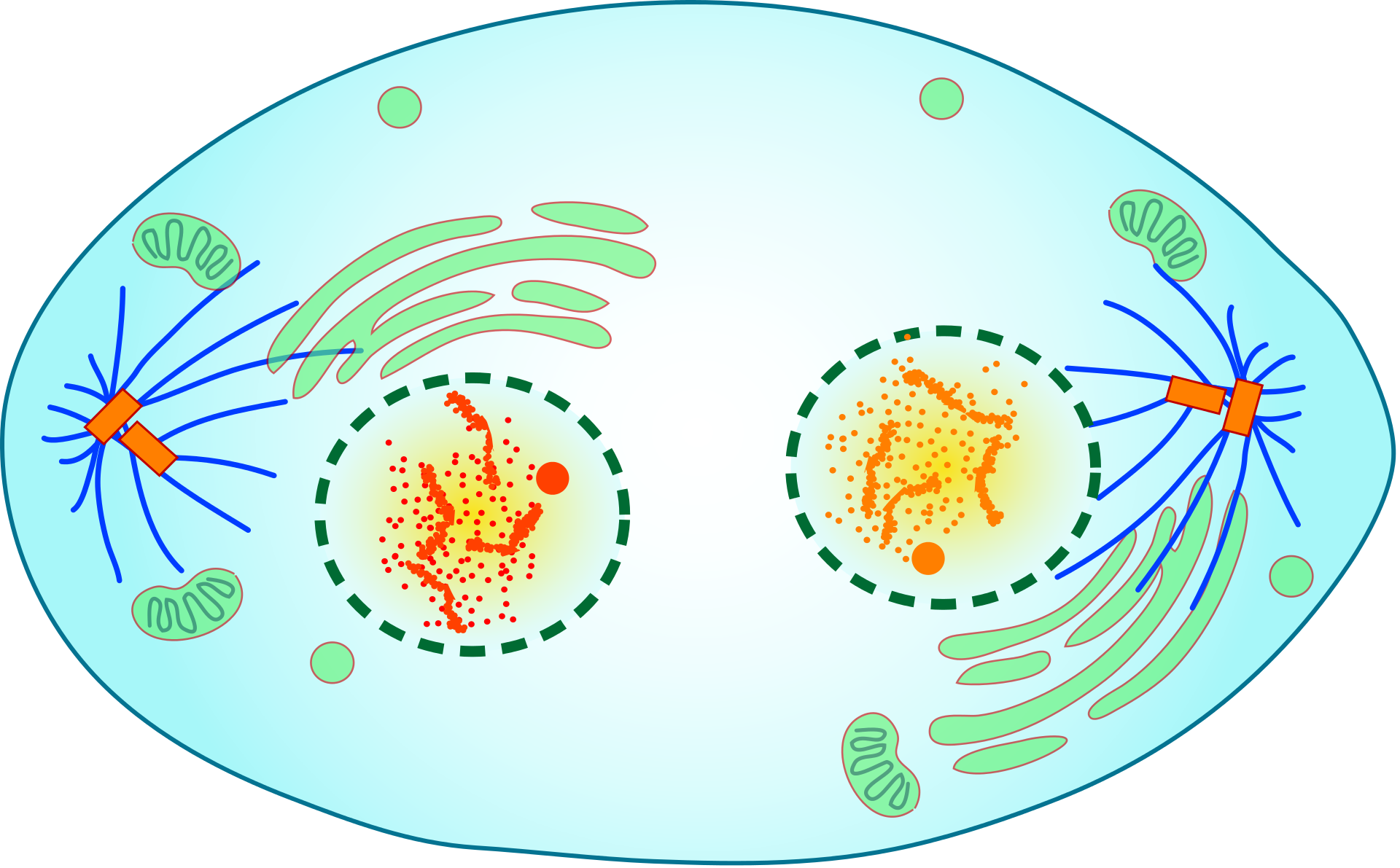
During telophase, the chromosomes begin to uncoil and form chromatin. This prepares the genetic material for directing the metabolic activities of the new cells. The spindle also breaks down, and new nuclear envelopes form.
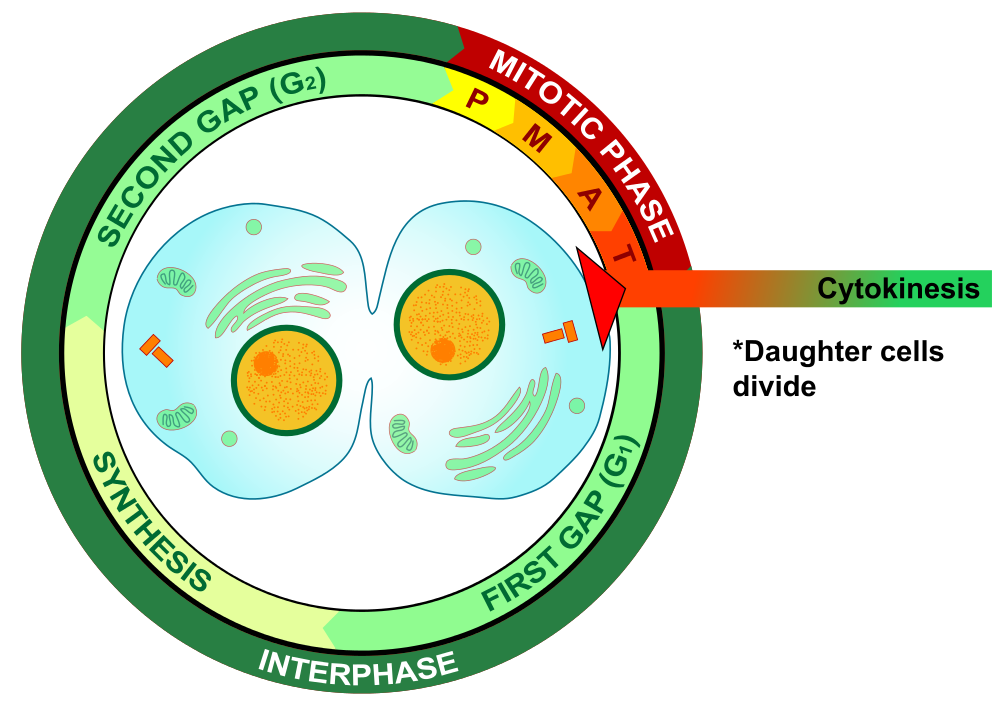
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis is the final stage of cell division. During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm splits in two and the cell divides, as shown below. In animal cells, the plasma membrane of the parent cell pinches inward along the cell’s equator until two daughter cells form. Thus, the goal of mitosis and cytokinesis is now complete, because one parent cell has given rise to two daughter cells. The daughter cells have the same chromosomes as the parent cell.
4.13 Summary
- Until a eukaryotic cell divides, its nuclear DNA exists as a grainy material called chromatin. After DNA replicates and the cell is about to divide, the DNA condenses and coils into the X-shaped form of a chromosome. Each chromosome actually consists of two sister chromatids, which are joined together at a centromere.
- Mitosis is the process during which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides. During this process, sister chromatids separate from each other and move to opposite poles of the cell. This happens in four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Cytokinesis is the final stage of cell division, during which the cytoplasm splits in two and two daughter cells form.
4.13 Review Questions
- Describe the different forms that DNA takes before and during cell division in a eukaryotic cell.
-
- Identify the four phases of mitosis in an animal cell, and summarize what happens during each phase.
- Order the diagrams of the stages of mitosis:
- Explain what happens during cytokinesis in an animal cell.
- What do you think would happen if the sister chromatids of one of the chromosomes did not separate during mitosis?
- True or False:
4.13 Explore More
Mitosis, NDSU Virtual Cell Animations project (ndsuvirtualcell), 2012.
Nondisjunction (Trisomy 21) – An Animated Tutorial, Kristen Koprowski, 2012.
Attributions
Figure 4.13.1
Anaphase_IF by Roy van Heesbeen on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 4.13.2
Chromosomes by OpenClipArt-Vectors on Pixabay is used under the Pixabay License (https://pixabay.com/service/license/).
Figure 4.13.3
Chromosome/ Chromatid/ Sister Chromatid by Christine Miller is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 4.13.4
Simple Mitosis by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal [LadyofHats] via CK-12 Foundation is used under a CC BY-NC 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) license.
 ©CK-12 Foundation Licensed under
©CK-12 Foundation Licensed under ![]() • Terms of Use • Attribution
• Terms of Use • Attribution
Figure 4.13.5
Mitotic Prophase [tiny] by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal [LadyofHats] on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 4.13.6
Prophase Eukaryotic Mitosis by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal [LadyofHats] on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 4.13.7
Mitotic_Metaphase by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal [LadyofHats] on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 4.13.8
Metaphase Eukaryotic Mitosis by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal [LadyofHats] on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 4.13.9
Anaphase [adapted] by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal [LadyofHats] on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 4.13.10
Anaphase_eukaryotic_mitosis.svg by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal [LadyofHats] on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 4.13.11
Mitotic Telophase by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal [LadyofHats] on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 4.13.12
Telophase Eukaryotic Mitosis by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal [LadyofHats] on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 4.13.13
Mitotic Cytokinesis by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal [LadyofHats] on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 4.13.14
Cytokinesis Eukaryotic Mitosis by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal [LadyofHats] on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
References
Koprowski, K., Cabey, R. [Kristen Koprowski]. (2012). Nondisjunction (Trisomy 21) – An Animated Tutorial. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EA0qxhR2oOk&feature=youtu.be
NDSU Virtual Cell Animations project [ndsuvirtualcell]. (2012). Mitosis. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C6hn3sA0ip0&t=21s
Cells which have a nucleus enclosed within membranes, unlike prokaryotes, which have no membrane-bound organelles.
The process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle.
Deoxyribonucleic acid - the molecule carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses.
A central organelle containing hereditary material.
A mass of genetic material composed of DNA and proteins that condense to form chromosomes during eukaryotic cell division.
A threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
Two identical copies formed by the DNA replication of a chromosome, with both copies joined together by a common centromere.
The region in a chromosome that attaches to a spindle fibre at metaphase of mitosis or meiosis.
The first stage of cell division in both mitosis and meiosis. Beginning after interphase, DNA has already been replicated when the cell enters prophase. The main occurrences in prophase are the condensation of the chromatin and the disappearance of the nucleolus.
A cylindrical organelle composed of microtubules located near the nucleus in animal cells, occurring in pairs and involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division.
A stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle in which condensed chromosomes align in the equator of the cell before being separated into each of the two daughter cells.
The stage of mitosis after metaphase and before telophase, when replicated chromosomes are split and the newly-copied chromosomes (daughter chromatids) are moved to opposite poles of the cell.
The final phase of cell division, between anaphase and interphase, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed.

